Back to article: Guidelines for DNA recombination and repair studies: Cellular assays of DNA repair pathways
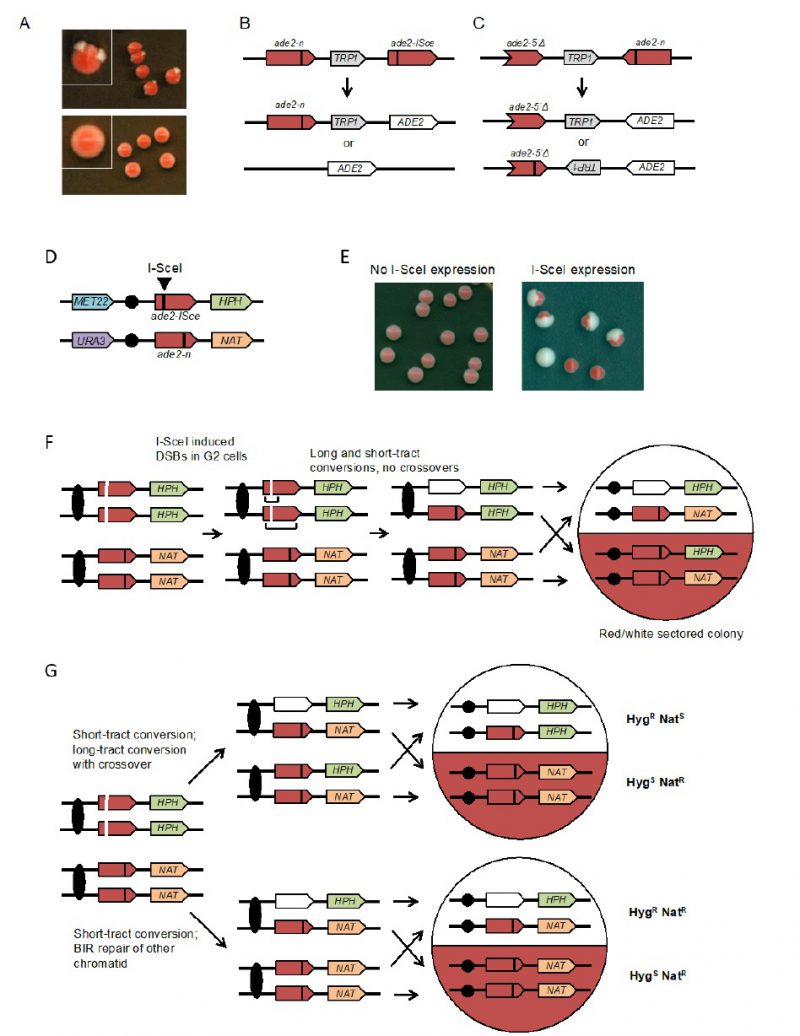
FIGURE 3: Colony color sectoring assays to detect spontaneous or DSB-induced recombination in haploid and diploids cells. (A) The upper panel shows wild-type colonies with the inverted-repeat reporter; rad52Δ (recombination-deficient) colonies are shown in the lower panel. (B) Direct-repeat recombination reporter: the ade2-n allele was generated by restriction enzyme fill-in of a NdeI site, the ade2-ISce allele was made by inserting the I-SceI cut site at the AatII site. Gene conversion events retain the TRP1 marker, whereas crossovers (CO) or SSA result in loss of TRP1. (C) Inverted-repeat recombination reporter: the ade2-n and ade2-5′Δ alleles are place in inverted orientation and separated by TRP1. Gene conversion events retain TRP1 in the original configuration, whereas CO or long-tract sister-chromatid conversion flips the orientation of TRP1. (D) Diploid with ade2-n and ade2-ISce heteroalleles, heterozygous markers 150 kb downstream of the ade2 loci and heterozygous markers on the other chromosome arm. (E) Examples of colonies before and after I-SceI induction. (F) I-SceI cuts both chromatids with the ade2-ISce allele in G2 cells and repair occurs by short or long tract conversion yielding ADE2 or ade2-n allele, respectively. If both conversion events are non-CO, the colony is white/red sectored and the two halves retain heterozygosity for HPH (hygromycin resistance) and NAT (nourseothricin resistance). (G) If repair of one chromatid is associated with a CO and the recombinant chromatids segregate to different daughter cells, reciprocal LOH is detected. Note that if the recombinant chromatids segregate to the same daughter cell at mitosis, the CO is not detected and this must be taken into account when calculating the frequency of CO. BIR results in a half sector that retains heterozygosity and the other has LOH of the HPH marker.