Back to article: Insights from the redefinition of Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide O-antigen and core-oligosaccharide domains
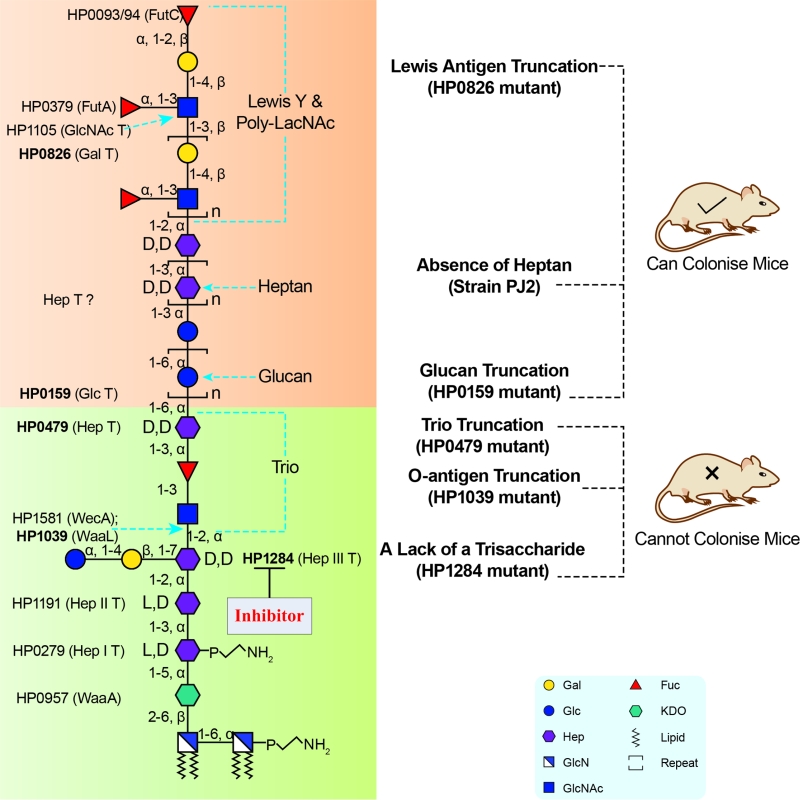
Figure 2: Inhibitor targeting the H. pylori LPS biosynthesis pathway. LPS struc-ture up to the Trio is conserved among H. pylori strains and required for colonisation. Thus, corresponding LPS biosynthetic enzymes involved in the assembly of the LPS conserved domains, such as HP1284, represent attractive virulence targets for the design of novel therapeutic agents for managing persistent H. pylori infection. Figure reproduced from Li et al. 2017 (doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006280) under the Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license.