Back to article: Untargeted metabolomics confirms and extends the understanding of the impact of aminoimidazole carboxamide ribotide (AICAR) in the metabolic network of Salmonella enterica
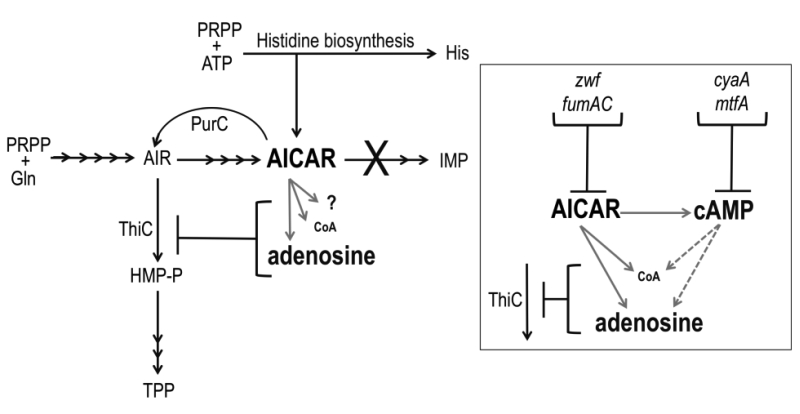
FIGURE 1: The role of AICAR in the purine histidine thiamine (PHT) metabolic network of S. enterica. Solid black arrows represent biochemical reactions; corresponding gene products are beside the reaction they catalyze. AICAR-mediated points of metabolic crosstalk that impact thiamine synthesis (ThiC activity) are indicated with gray arrows. Inset: AICAR accumulation leads to elevated cAMP. Elevated AICAR and cAMP independently decrease pantothenate (CoA) pools and increase adenosine pools demonstrating that these pools are subject to direct (solid lines) and indirect (dashed lines) effects of AICAR accumulation. These altered pools potentially contribute to decreased ThiC activity; loss of function mutations (zwf, fumAC, cyaA, mtfA) modulated AICAR and/or cAMP levels and restored thiamine synthesis.