Back to article: Fat storage-inducing transmembrane (FIT or FITM) proteins are related to lipid phosphatase/phosphotransferase enzymes
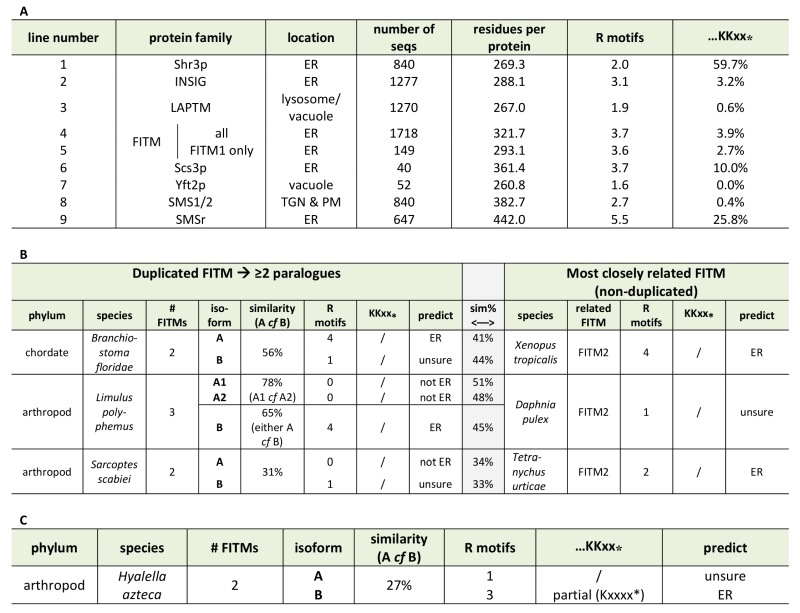
Table 1. ER retention motifs in FITM proteins.
(A) ER retention motifs (both di-arginine and C-terminal di-lysine) were compared across multiple large protein families (see Methods). Lines 1-3: examples of ER and lysosomal/vacuolar proteins; 4-7: FITM proteins – all and different subgroups; 8/9: Sphingomyelin synthase subgroups. (B) ER retention motifs were used to predict location in three recently duplicated FITM paralogues. Left-hand side: paralogues, including % similarity to each other; right-hand side: the FITM sequence in the most closely related organism, with central shaded column indicating % similarity between sequences on left- and right- hand sides. Prediction of location based on motifs: C-terminal di-lysine or ≥2 di-arginines = ER, 1 di-arginine = unsure, no di-arginines = not ER. (C) As B, showing one duplicated FITM pair, where the duplication appears to pre-date many speciation events, making it impossible to identify a single FITM that resembles the presumed antecedent.