Back to article: Shepherding DNA ends: Rif1 protects telomeres and chromosome breaks
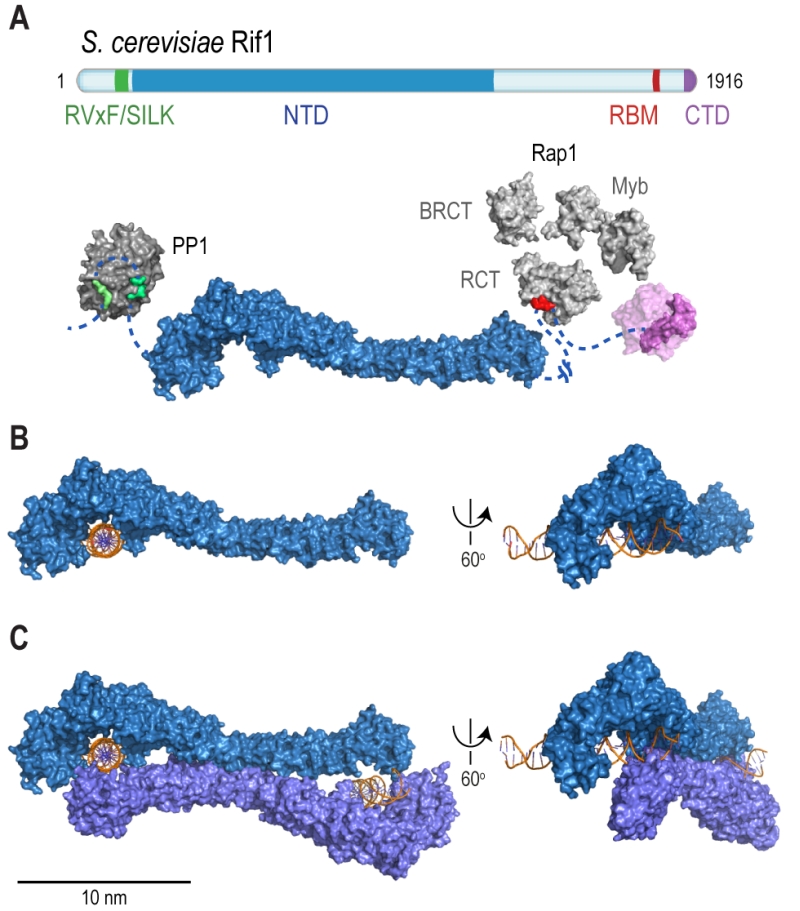
FIGURE 2: Rif1 domains and structural features. (A) Cartoon of S. cerevisiae Rif1 with structural representation of the indicated domains: RVxF/SILK PP1/Glc7 interacting motifs (green), NTD (N-terminal domain; blue), RBM (Rap1-binding motif; red) and CTD (C-terminal domain; purple). The RVxF (residues 115-118) and SILK (residues 146-149) motifs are shown bound with protein phosphatase PP1 (dark grey), modelled on two available co-crystal structures (PDB: 4G9J for RVxF, serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit, Homo sapiens [176] and PDB: 2O8A for SILK, serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-gamma catalytic subunit, Rattus norvegicus [177]). A flexible linker connects the RVxF and SILK motifs with the NTD (residues 188-1766), which is shaped like a shepherd’s crook (PDB: 5NVR [19]). The NTD connects via a 462 residue unstructured linker with RBM (residues 1752-1772). A co-crystal structure of RBM with the Rap1 C-terminal domain (RCT) is depicted (PDB: 4BJT). In addition, Rap1 contains BRCT and Myb domains (represented in light grey, Rap1 linker regions between structured domains not shown). CTD (C-terminal domain of Rif1, residues 1857-1916, PDB: 4BJS [22]) is a tetramerization domain, allowing oligomerization with other Rif1 molecules (as indicated in translucent purple). (B) The NTD of Rif1 in complex with dsDNA. (C) Rif1NTD bound with two distinct DNA molecules in the head-to-tail dimer conformation observed in Rif1-DNA co-crystals and in solution. Contacts with the DNA are made by the concave surface of the so-called HOOK domain at the N-terminal end of the NTD [19].
19. Mattarocci S, Reinert JK, Bunker RD, Fontana GA, Shi T, Klein D, Cavadini S, Faty M, Shyian M, Hafner L, Shore D, Thoma NH, Rass U (2017). Rif1 maintains telomeres and mediates DNA repair by encasing DNA ends. Nat Struct Mol Biol 24(7): 588-595. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3420
22. Shi T, Bunker RD, Mattarocci S, Ribeyre C, Faty M, Gut H, Scrima A, Rass U, Rubin SM, Shore D, Thoma NH (2013). Rif1 and Rif2 shape telomere function and architecture through multivalent Rap1 interactions. Cell 153(6): 1340-1353. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.007
176. Chatterjee J, Beullens M, Sukackaite R, Qian J, Lesage B, Hart DJ, Bollen M, Kohn M (2012) Development of a peptide that selectively activates protein phosphatase-1 in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51(40): 10054-10059. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201204308
177. Hurley TD, Yang J, Zhang L, Goodwin KD, Zou Q, Cortese M, Dunker AK, DePaoli-Roach AA (2007) Structural basis for regulation of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem 282(39): 28874-28883. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M703472200