Back to article: Snf1 cooperates with the CWI MAPK pathway to mediate the degradation of Med13 following oxidative stress
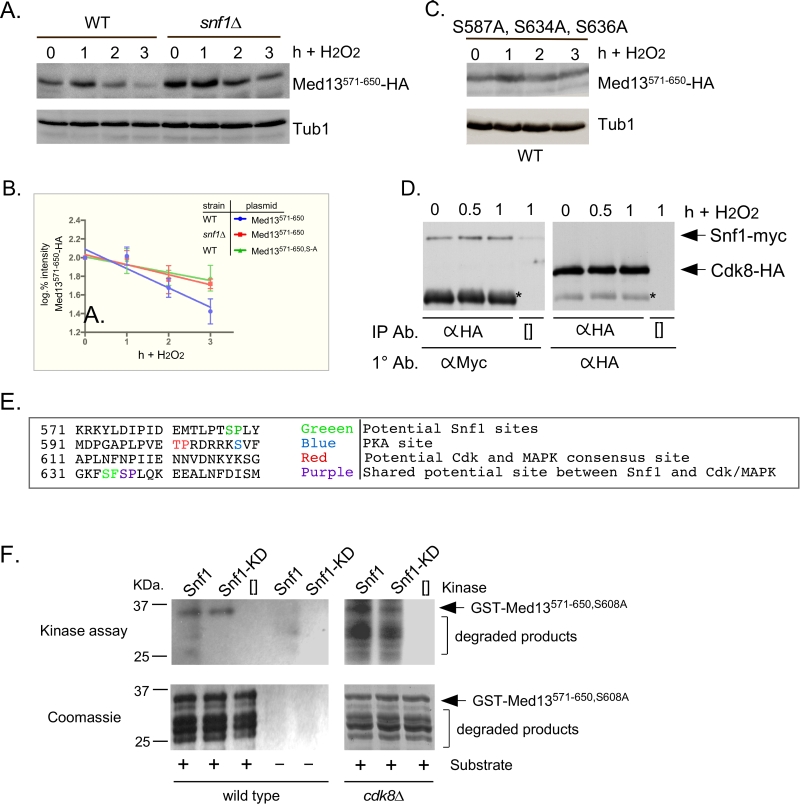
FIGURE 5: Snf1 phosphorylates degron571-650. (A) Mid-log wild-type (RSY10) or snf1∆ cultures (RSY202) harboring degron571-650 (pDS15) were subjected to an H2O2 timecourse experiment and protein extracts analyzed by Western blot. Tub1 levels were used as loading controls. (B) Degradation kinetics of degron571-650 shown in A and C. Values represent averages ± SD from a total of at three Western blots from independent experiments. (C) As in A except that degron571-650,S587A, S634A, S636A (pDS56) was analyzed in wild-type cells. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of Snf1-myc and Cdk8-HA. Mid log wild-type cells harboring Snf1-myc and Cdk8-HA on single copy plasmids were treated with 0.4 mM H2O2 for the timepoints shown. Protein extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA, separated by SDS-PAGE Western analysis and the membrane probed with the antibodies shown. [] represents no IP antibody and the asterisk represents the heavy chain. See Fig. S3C for vector control. (E) Potential phospho-sites in Med13571-650. (F) Upper panels: Kinase assays using Snf1 and Snf1K84R-myc (kinase dead) immunoprecipitated from yeast protein extracts prepared from either wild type (left panel) or cdk8∆ cells (right panel) and Med13-degron571-650 (GST-Med13571-906,S608A purified from E. coli) as the substrate. The reactions were separated by SDS PAGE and subject to autoradiography. Lower panels: Coomassie stained gels showing the input used in the kinase assays.