Back to article: A Cinderella story: how the vacuolar proteases Pep4 and Prb1 do more than cleaning up the cell’s mass degradation processes
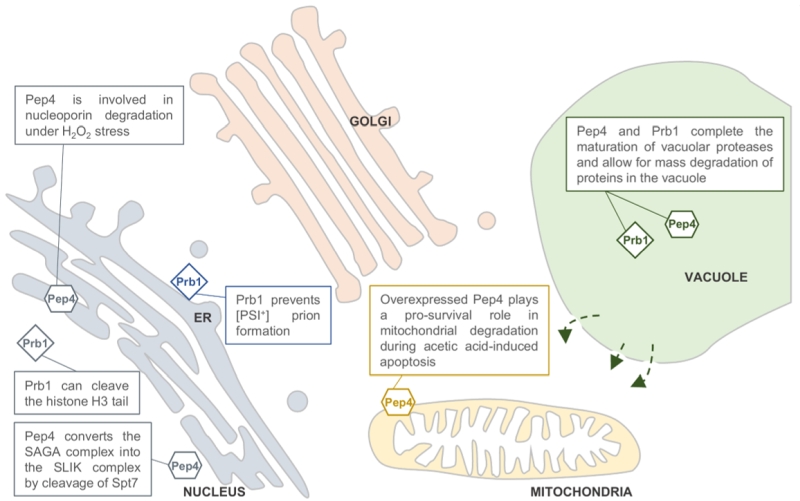
FIGURE 1: Predicted locations of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pro-teases Pep4 and Prb1. Both proteases are well known for their role in protein degradation in the vacuole. Pep4 and Prb1 share a prominent role in the proteolytic activation and maturation of most vacuolar proteases, including themselves. Under stress conditions, the permeability of the vacuolar membrane has been reported to increase. This might enable the proteases to escape the vacuole and locate to other sites in the cell (indicated by arrows). It has been reported that Pep4 is associated with mitochondrial degradation under acetic acid-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, it has been described that nucleoporins are degraded by Pep4 in H2O2-induced cell death, sug-gesting a nucleus-associated localization. This idea is strengthened by the importance of Pep4 in the generation of the SAGA-like (SLIK) complex by cleavage of the Spt7 component of the SAGA complex. It was found that the conserved pro-cess of H3 clipping, altering gene expression, was performed by the Prb1 protease in S. cerevisiae, also sug-gesting a nuclear localization for Prb1. Furthermore, Prb1 was shown to inhibit [PSI+] prion formation. Okamoto et al. [25] hypothesize that prevention of prion formation by cleavage of the Sup35 protein takes place on actively translating ribosomes. It should be noted that the non-vacuolar localizations of Pep4 and Prb1 were never confirmed in vivo by conclusive experimental results.
25. Okamoto A, Hosoda N, Tanaka A, Newnam GP, Chernoff YO, Hoshino SI (2017). Proteolysis suppresses spontaneous prion generation in yeast. J Biol Chem 292(49): 20113-20124. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.811323