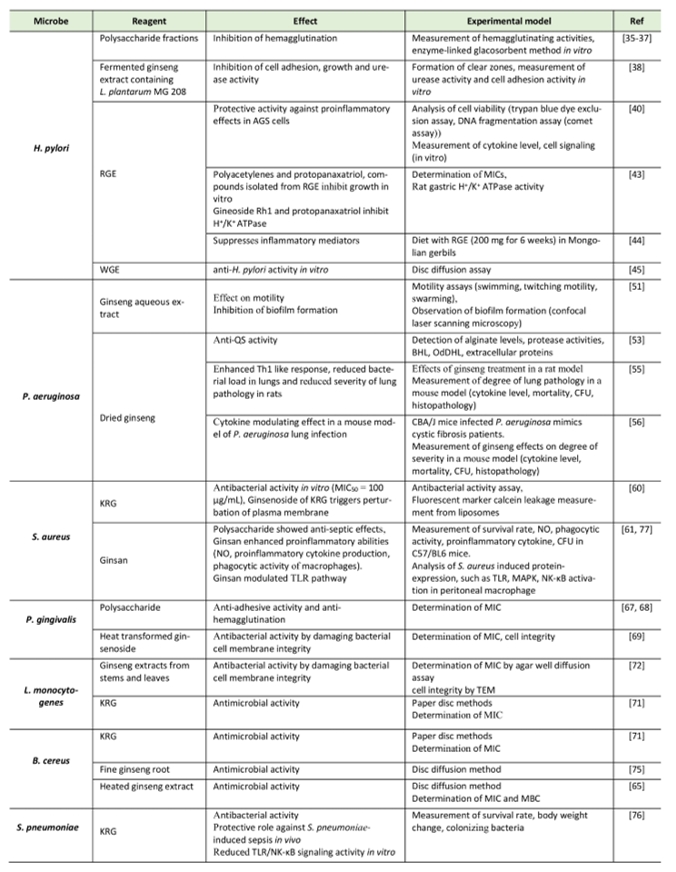
Back to article: Protective roles of ginseng against bacterial infection
Abbreviations: KRG: Korean red ginseng, MBC: minimum bactericidal concentration, MIC: minimum inhibitory concentration, RGE: red ginseng extract, TEM: transmission electron microscopy.
35. Belogortseva NI, Yoon JY, Kim KH (2000). Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori hemagglutination by polysaccharide fractions from roots of Panax ginseng. Planta Med 66(3):217-220. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10821045
36. Woo JS, Ha BH, Kim TG, Lim YH, Kim KH (2001). Development of an enzyme-linked glycosorbent method to monitor the inhibition of sialic acid-dependent Helicobacter pylori adhesion. Biotechnol Lett 23(7):507-511. http://dx.doi.org/10.1023/A:1010360412969
37. Lee JH, Eun KP, Uhm CS, Chung MS, Kyung HK (2004). Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori adhesion to human gastric adenocarcinoma epithelial cells by acidic polysaccharides from Artemisia capillaris and Panax ginseng. Planta Med 70(7):615-619. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15254854
38. Yang JW, Choi SY, Park SJ, Paek NS, Kim SS (2012). Anti-Helicobacter Pylori Effect of Fermented Ginseng Extracts with Lactobacillus plantarum MG 208. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 55(1):53-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13765-012-0009-0
40. Park S, Yeo M, Jin JH, Lee KM, Jung JY, Choue R, Cho SW, Hahm KB (2005). Rescue of Helicobacter pylori-Induced Cytotoxicity by Red Ginseng. Dig Dis Sci 50(7):1218-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2763-x
44. Bae M, Jang S, Lim JW, Kang J, Bak EJ, Cha JH, Kim H (2014). Protective effect of Korean red ginseng extract against Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation in Mongolian gerbils. J Ginseng Res 38(1):8-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.005
45. Jee HS, Chang KH, Moon SH, Park SH, Paik HD (2008). Anti-Helicobacter pylori, Cytotoxic, and Anti-inflammatory Activities of White Ginseng Extract. Food Sci Biotechnol 17(5):1106-1109.
51. Wu H, Lee B, Yang L, Wang H, Givskov M, Molin S, Høiby N, Song Z (2011). Effects of ginseng on Pseudomonas aeruginosa motility and biofilm formation. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 62(1):49-52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00787.x
55. Song Z, Krogh Johansen H, Faber V, Moser C, Kharazmi A, Rygaard J, Høiby N (1997). Ginseng Treatment Reduces Bacterial Load and Lung Pathology in Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pneumonia in Rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41(5):961-964. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=9145852
56. Song Z, Moser C, Wu H, Faber V, Kharazmi A, Høiby (2003). Cytokine modulating effect of ginseng treatment in a mouse model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection. J Cyst Fibros 2(3):112-119. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1569-1993(03)00065-1
60. Sung WS, Lee DG (2008). The combination effect of Korean red ginseng saponins with kanamycin and cefotaxime against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biol Pharm Bull 31(8):1614-1617. http://dx.doi.org/10.1248/bpb.31.1614
61. Lim DS, Bae KG, Jung IS, Kim CH, Yun YS, Song JY (2002). Anti-septicaemic effect of polysaccharide from Panax ginseng by macrophage activation. J Infect 45(1):32-38. http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/jinf.2002.1007
65. Na S, Kim JH, Rhee YK, Oh SW (2017). Enhancing the antimicrobial activity of ginseng against Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus by heat treatment. Food Sci Biotechnol 27(1):203-210. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0209-9
67. Lee JH, Lee JS, Chung MS, Kim KH (2004). In Vitro Anti-Adhesive Activity of an Acidic Polysaccharide from Panax ginseng on Porphyromonas gingivalis Binding to Erythrocytes. Planta Med 70(6):566-569. http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-827160
68. Lee JH, Shim JS, Lee JS, Kim MK, Chung MS, Kim KH (2006). Pectin-like acidic polysaccharide from Panax ginseng with selective antiadhesive activity against pathogenic bacteria. Carbohydr Res 341(9):1154-1163. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2006.03.032
69. Xue P, Yao Y, Yang XS, Feng J, Ren GX (2017). Improved antimicrobial effect of ginseng extract by heat transformation. J Ginseng Res 41(2):180-187. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2016.03.002
71. Choi YH, Kim SE, Huh J, Han YH, Lee MJ (2012). Antibacterial and Antioxidative Activity of Roasted Coffee and Red Ginseng Mixture Extracts. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr 41(3):320-326. http://dx.doi.org/10.3746/jkfn.2012.41.3.320
72. Lee KA, Kim WJ, Kim HJ, Kim KT, Paik HD (2013). Antibacterial activity of Ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer) stems-leaves extract produced by subcritical water extraction. Int J Food Sci Technol 48(5):947-953. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.12046
75. Lim JK, Kang HJ, Kang SN, Lee BY (2009). Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of various solvent fractions of fine ginseng root. Food Sci Biotechnol 18(2):513-518. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=KR2010003264
76. Nguyen CT, Luong TT, Lee SY, Kim GL, Kwon H, Lee HG, Park CK, Rhee DK (2015). Panax ginseng aqueous extract prevents pneumococcal sepsis in vivo by potentiating cell survival and diminishing inflammation. Phytomedicine 22(11):1055-1061. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2015.07.005
77. Ahn JY, Choi IS, Shim JY, Yun EK, Yun YS, Jeong G, Song JY (2006). The immunomodulator ginsan induces resistance to experimental sepsis by inhibiting Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory signals. Eur J Immunol 36(1):37-45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/eji.200535138