Back to article: D-Serine reduces the expression of the cytopathic genotoxin colibactin
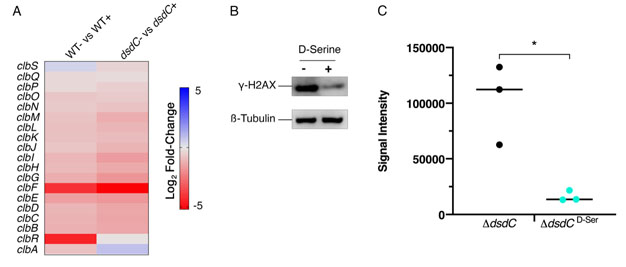
FIGURE 6: Deletion of dsdC does not affect D-Serine associated repression of colibactin. Generation of an isogenic mutant, Nissle ΔdsdC, revealed that D-Serine-associated repression of colibactin activity occurred independently of the D-Serine tolerance locus in pks+ E. coli strains. (A) Heat map showing the EdgeR calculated log2 relative fold changes for each gene in the pks island with corresponding colour key adjacent. False discovery rate-corrected P values can be found in Table S1. (B) The genotoxic activity of Nissle ΔdsdC was assessed by infecting HeLa cells as discussed above. Proteins were extracted and the level of H2AX phosphorylation was determined. Immunoblot analysis of cell lysates extracted 4 h post-infection is shown. Anti-γ-H2AX antibody was used as an indicator of double stranded DNA breaks and β-Tubulin was used as a loading control for cell lysates. (C) Signal intensities of bands were measured as described in the methods using LI-COR Image Studio. γ-H2AX signals were corrected to account for any variation in loading using β-Tubulin signal intensity. Experimental signal was normalized so that the mean signal intensity of the samples was equivalent for each experiment. The experiment was carried out in triplicate. Columns represent mean +/- SEM with individual experimental observations indicated by data points. Statistical significance was assessed by unpaired Student's t-test with, * indicating P < 0.05.