Back to article: The cAMP-PKA signalling crosstalks with CWI and HOG-MAPK pathways in yeast cell response to osmotic and thermal stress
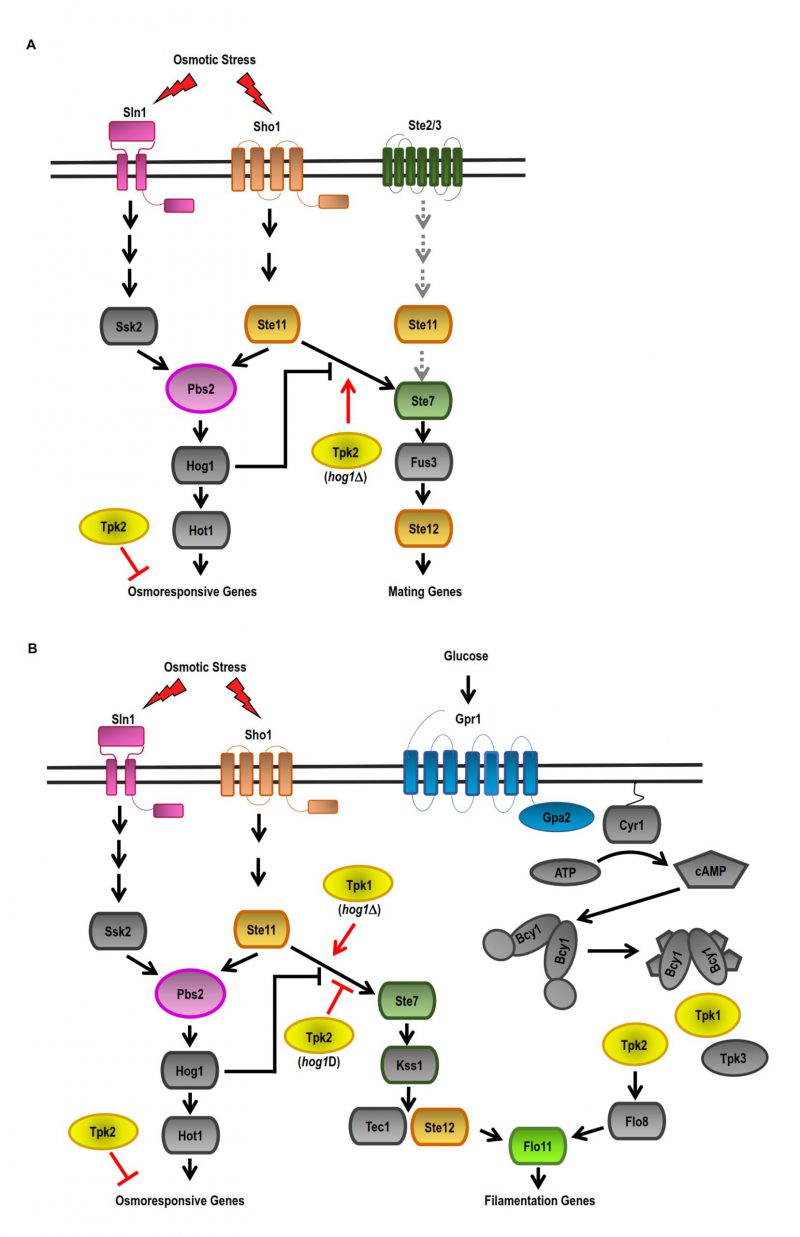
FIGURE 1: Model of the crosstalk between cAMP-PKA and HOG pathways in response to osmotic stress. (A) Two independent osmosensing mechanisms, the Sln1 and Sho1 branches, lead to the activation of specific kinases Ssk2/22 and Ste11 (MAPKKK) that converge on the common MAPKK Pbs2, which activates the Hog1 MAPK. In response to osmotic stress, Hog1 inhibits the crosstalk with the pheromone MAPK pathway (pMAPK) via inhibition of the MAPKKK Ste11 of the SHO1 branch. Upon HOG1 deletion (hog1Δ), the crosstalk between the HOG-MAPK and pMAPK pathways can be positively regulated by Tpk2. (B) In response to osmotic stress, Hog1 inhibits the crosstalk of the filamentous MAPK pathway (fgMAPK) by inhibiting the MAPKKK Ste11 of the SHO1 branch. In a hog1Δ background, Tpk2 negatively regulates the crosstalk between the HOG-MAPK and fgMAPK pathways, while Tpk1 positively regulates the crosstalk between the HOG-MAPK and fgMAPK pathways in response to osmotic stress. In the presence of glucose, Tpk2 positively regulates invasive growth.