Back to article: Polyadenylated versions of small non-coding RNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are degraded by Rrp6p/Rrp47p independent of the core nuclear exosome
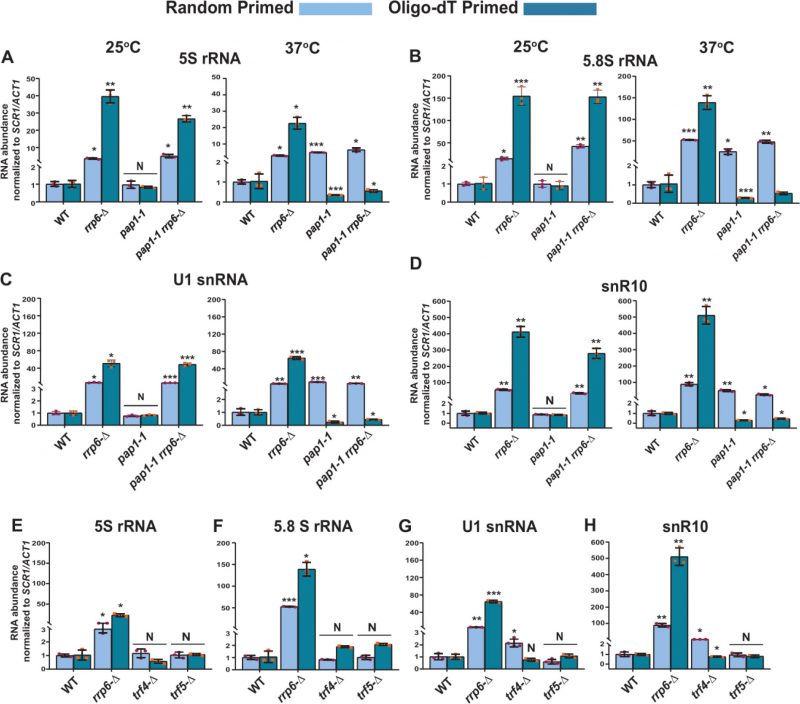
FIGURE 6: Both the canonical Poly(A) polymerase Pap1p and non-canonical Poly(A) polymerase Trf4p play a vital role in the polyadenylation of the sncRNAs. Scattered/Bar plot revealing the steady-state levels of 5S, 5.8S, U1, and snR10 RNAs estimated from the 2 ng cDNA samples prepared using random hexanucleotide primers (sky blue bars) or oligo-dT30 anchor primer (indigo blue bars) by RT-qPCR from WT strain (yBD-161) and strains carrying mutations in the RRP6 (rrp6-Δ, yBD-162), PAP1 (pap1-1, yBD-163), RRP6 and PAP1 (pap1-1 rrp6-Δ, yBD-179) (panels A-D) or WT (yBD-263), RRP6 (rrp6-Δ) (yBD-265), TRF4 (trf4-Δ) (yBD-306), TRF5 (trf5-Δ) (yBD-334) genes (panels E-H). The pap1-1 and pap1-1 rrp6-Δ strains were pre-grown at 25°C, followed by splitting the culture into two halves. Half of the culture continued to grow at 25°C for 2 hours and a 2-hour shift to 37°C were performed on the other half of the culture before harvesting them. Total RNA and cDNA isolation from them followed by RT-qPCR reaction carried out as described in materials and methods. SCR1 (in the case of Random Primer) and ACT1 mRNA (in the case of oligo dT30 primer) were used as the internal loading control. Normalized values of each of the ncRNAs in the WT yeast strain were set to 1. Three independent cDNA preparations (biological replicates, n = 3) were used to determine the levels of various ncRNAs. The statistical significance of difference reflected in the ranges of P values estimated from Student’s two-tailed t-tests for a given pair of test strains for every message are presented with the following symbols, *<0.05, **<0.005, and ***<0.001; N, not significant.