Back to article: Fecal gelatinase does not predict mortality in patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis
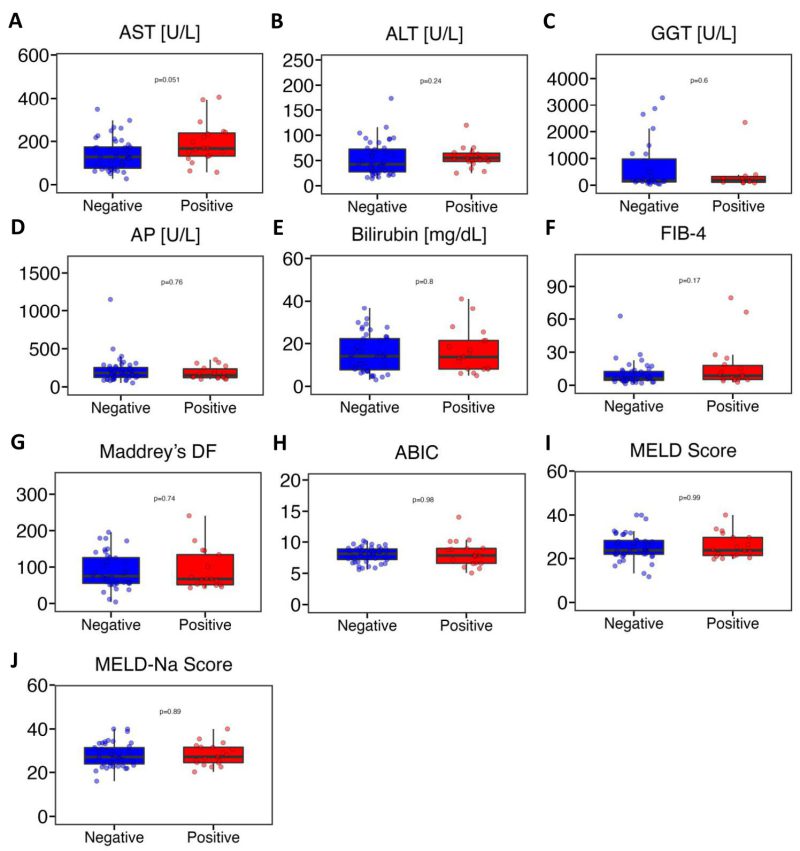
FIGURE 3: Fecal gelatinase positive patients with alcohol-associated hepatitis do not have more severe liver disease than gelatinase negative patients. (A) AST (n=64). (B) ALT (n=63). (C) GGT (n=38). (D) AP (n=63). (E) Bilirubin (n=64). (F) FIB-4 (n=62). (G) Maddrey’s DF (n=56). (H) ABIC (n=64). (I) MELD score (n=64). (J) MELD-Na score (n=64). ABIC, ‘Age, serum bilirubin, INR, and serum creatinine score’; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AP, alkaline phosphatase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; FIB-4, Fibrosis-4 Index; GGT, gamma-glutamyltransferase; HE, hepatic encephalopathy; INR, international normalized ratio; Maddrey’s DF, Maddrey’s Discriminant Function; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; MELD-Na, sodium-adjusted model for end- stage liver disease. P value of equal or less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.