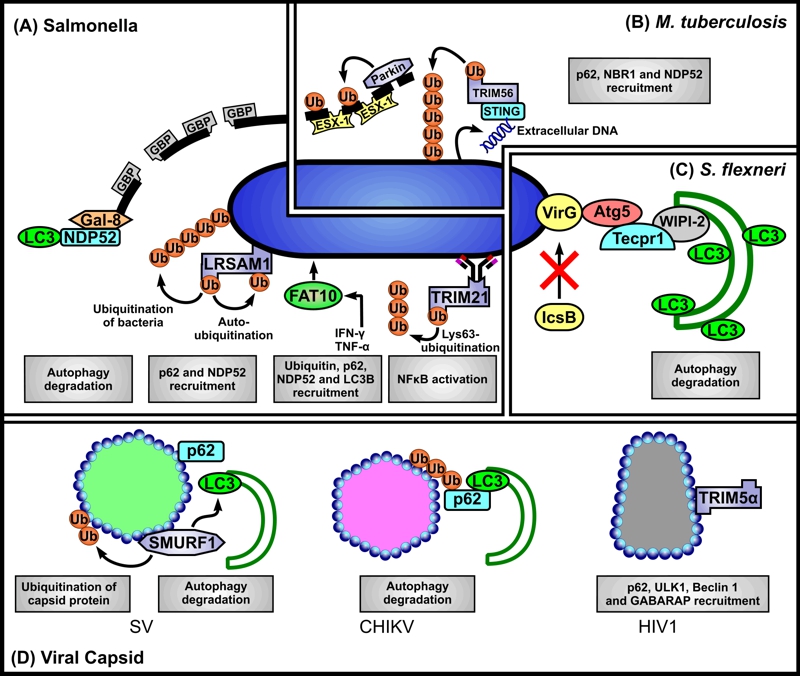
FIGURE 1: Scenarios for SLR-dependent autophagy induction.
(A) Salmonella. Autophagic clearance of Salmonella that have ‘escaped’ from phagosomes, or reside in permeabilised phagosomes may be mediated via several scenarios. First, Salmonella-containing phagosome membrane segments that occur as a consequence of loss of membrane integrity, in part mediated by guanylate-binding proteins (GBPs), are targeted by direct binding of galectin 8 (Gal-8) and subsequent binding of NDP52 leading to their recognition as autophagosome cargo. Second, the E3 ligase LRSAM1 can recognise as yet unidentified conserved regions of bacterial surface components. Bacterial proteins are ubiquitinated by LRSAM1, but their identity also remains to be established. Auto-ubiquitination of LRSAM1 at internal lysine residues is implicated in p62 recruitment. Additionally NDP52 is recruited to bacteria. Third, simultaneous decoration of bacteria with FAT10, ubiquitin, p62, NDP52 and LC3B may occur, but it is unclear whether FAT10 binds directly to bacterial structures, or to cellular structures proximal to, or surrounding them. Fourth, antibody-bound bacteria may interact with TRIM21 whose RING domain catalyses formation of free K63 ubiquitin chains required for downstream NFκB-stimulated inflammatory response and LC3 recruitment.
(B) M. tuberculosis. The E3 ligase Parkin catalyses Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of bacteria-containing phagosome membrane segments which have been permeabilised by the secreted mycobacterial effector system ESX-1 (early secretory antigenic target 6 system 1). Subsequently p62, NBR1 and NDP52 are recruited for delivery of the ‘marked’ membranes to autophagosomes. Additionally, bacteria ‘exposed’ to the cytosol can elicit the host cytosolic DNA sensing pathway through bacteria-intrinsic surface-located extracellular DNA that is recognised by stimulator of interferon gene 1 (STING). STING is targeted by TRIM56 which catalyses Lys-63 ubiquitination of STING-targeted bacteria subsequently leading to the recruitment of p62, NDP52 and TBK1 to mediate autophagy.
(C) S. flexneri. Atg5 binds the bacterial surface protein IcsA of bacteria lacking IcsB (IcsB-) thereby targeting them for autophagy. Tectonin domain-containing protein (Tecpr1) bridges between the Atg5-targeted bacteria and the WIPI2-positive phagophore membrane.
(D) Viral capsids. Direct interaction of p62 and of the SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin ligase 1 (SMURF-1) with Sindbis virus (SV) capsid protein is required for the subsequent recruitment of LC3. Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) capsid is ubiquitinated, bound by p62 and targeted to autophagy, however capsid ubiquitination appears to be independent of SMURF-1. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) p24 capsid is directly recognised by TRIM5α (without a need for ubiquitination) and delivered it to autophagosomes. TRIM5α binding to capsid also mediates interactions with several autophagy-associated components, including p62, ULK1, Beclin 1 and GABARAP.