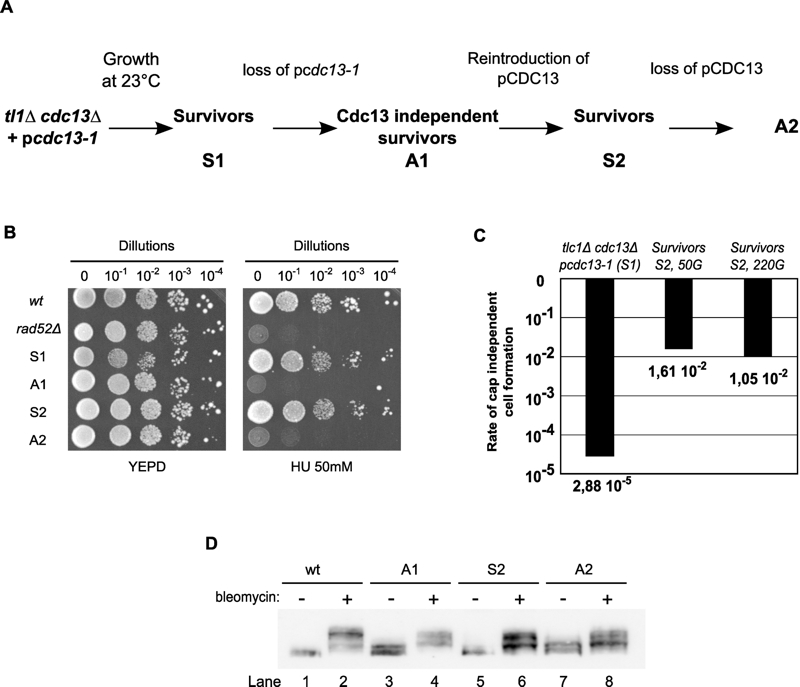
FIGURE 5: The process of generating Cdc13-independent survivors (cdc13Δ-cells) comprises a reversible component.
(A) Schematic representation of the procedure used to generate S2 survivors and second generation cdc13Δ-A2 of Cdc13-independent survivors. S1 survivors and cdc13Δ-A1 were generated as described in Fig. 1. S2 survivor cells were derived from cdc13Δ-A1. These cells were grown for up to 220 generations (220G) after transformation with the plasmid carrying the cdc13-1 allele. For cdc13Δ-A2 cells (MLY123), the loss of the pCDC13 plasmid was verified by growing cells on FOA synthetic medium.
(B) Cells identified with symbols as in (A) were spotted onto YEPD plates with or without hydroxyurea (HU) and incubated for 72 h at 23°C. A haploid rad52Δ strain was used as control for HU sensitivity.
(C) Rate of successful cdc13-independent cell formation (calculated by fluctuation test) for survivors S1 (MLY112) and survivors S2 (MLY122 + pcdc13-1). S2 survivors were grown for 50 or 220 generations after pcdc13-1 introduction and before the fluctuation test for plasmid loss was performed.
(D) Western blot of whole cell protein extracts prepared from strains indicated with the same symbols as in (A)(top). Cell treatment with bleomycin is indicated with – and +, and the blot was probed with an anti-Rad52 antibody as in Fig. 1.