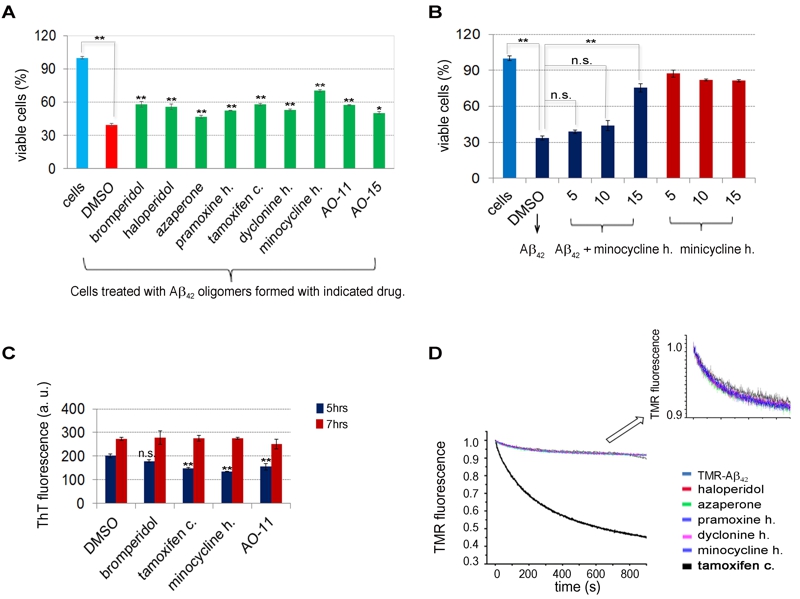
FIGURE 4: The protective effect of drugs on Aβ42 induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells.
(A) Toxicity of Aβ42 assembled under conditions favoring oligomer formation was reduced when assembly was done in the presence of drugs. Aβ42 at 200 μM assembled under conditions favoring oligomer formation in the presence of 100 μM drug or DMSO was diluted and added to PC12 cells at a concentration of 20 μM Aβ42 and 10 μM drug. Cell viability was assessed after 24 hrs growth at 37°C using the MTT assay. The percentage of viable cells is shown. Error bars are the standard deviation of triplicate experiments.
(B) Dose-dependent effects of minocycline HCl on Aβ42 associated cytotoxicity. Methods were as in (A). PC12 cells were treated with final concentrations of 20 μM Aβ42 with 5, 10, and 15 µM minocycline HCl or DMSO only (blue bars). Cells were also treated with the indicated amount of minocycline HCl alone (red bars).
(C) Effect of drugs on in vitro Aβ42 high molecular fibril assembly in fibril favorable conditions. Aβ42 was assembled into high molecular fibrils at 37°C in the presence of 50 µM drug or control DMSO according to [42]. Thioflavine T (ThT) was added to aliquots at the indicated times and fluorescence, indicative of fiber formation, was measured.
(D) Effect of drugs on in vitro labeled Aβ42 (TMR-K-Aβ42) oligomerization. Reduced TMR fluorescence, which measures oligomerization, was recorded as a function of time immediately after dilution of the TMR-K-Aβ42 with addition of 10 µM of each drug or DMSO for a negative control. The asterisks show significance levels of **P < 0.01 or *P < 0.05 according to Student’s t test between DMSO control and drug treatment (A) and DMSO control and drug treatment at 5 hrs (C).