Back to article: The ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, Ubc1, indirectly regulates SNF1 kinase activity via Forkhead-dependent transcription
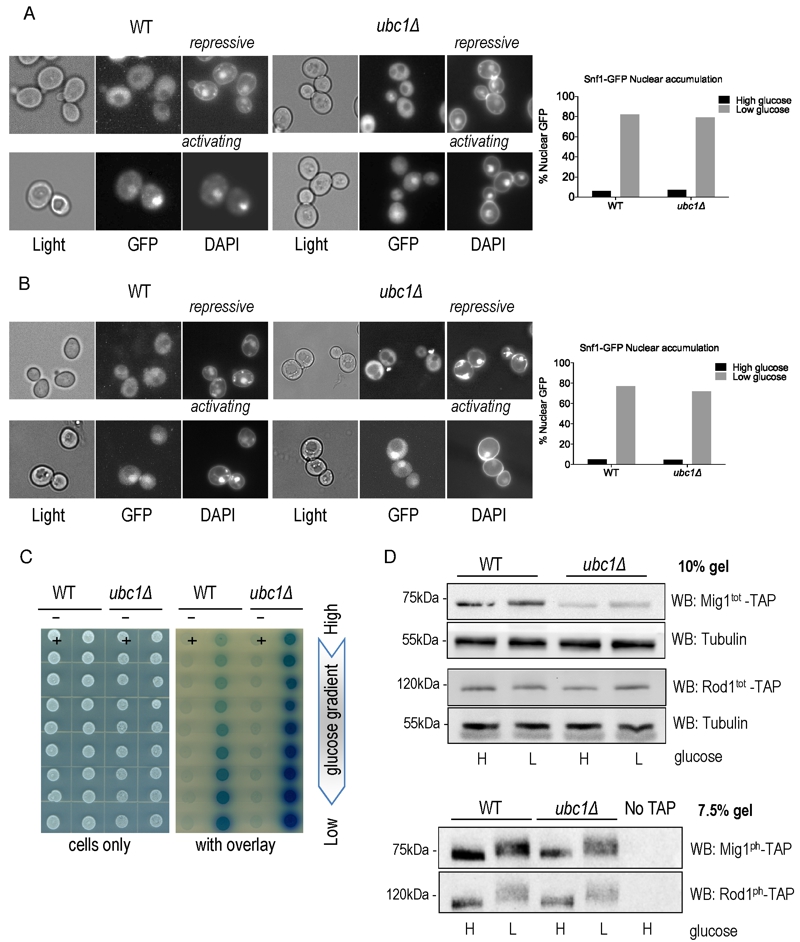
FIGURE 2: Loss of Ubc1 function does not impair SNF1 kinase nuclear accumulation, allosteric associations or substrate targeting.
(A) Fluorescent microscopy of GFP-tagged yeast Snf1 constitutively expressed from a high copy 2μ plasmid or (B) expressed from the endogenous Snf1 promoter in isogenic WT and ubc1Δ strains grown under repressive (2% glucose) or shifted to activating (5% glycerol for 30 minutes) conditions. The percent of cells with Snf1-GFP nuclear accumulation was quantitated from four biological repeats. 125 consecutive cells were scored for co-localization of GFP and DAPI signal in high and low glucose in the isogenic WT and ubc1Δ strains.
(C) 2-hybrid associations between empty vectors (-) and Snf1-Snf4 pairs (+) in WT and ubc1Δ strains are shown. Equal cell numbers were spotted down a glucose gradient (0.05% to 2% glucose) before and after β-galactosidase color development from overlay.
(D) Isogenic WT and ubc1Δ strains harboring endogenous TAP-epitope tags to Mig1 and Rod1 were divided into high (H: 2%) and low (L: 0.05%) glucose media for 30 minutes prior to cell lysis. Duplicate sample were run in parallel on 10% acrylamide gels (for total TAP-protein; Mig1tot and Rod1tot, upper panels) and 7.5% (to enhance the phospho-shift; Mig1ph and Rod1ph, lower panels).
WB: Western Blot primary antibody/target. Light: non fluorescent 100 x objective. GFP: green fluorescent protein epitope tag. DAPI: (4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole, Dihydrochloride) a fluorescent DNA interchelator.