Back to article: The copper transport-associated protein Ctr4 can form prion-like epigenetic determinants in Schizosaccharomyces pombe
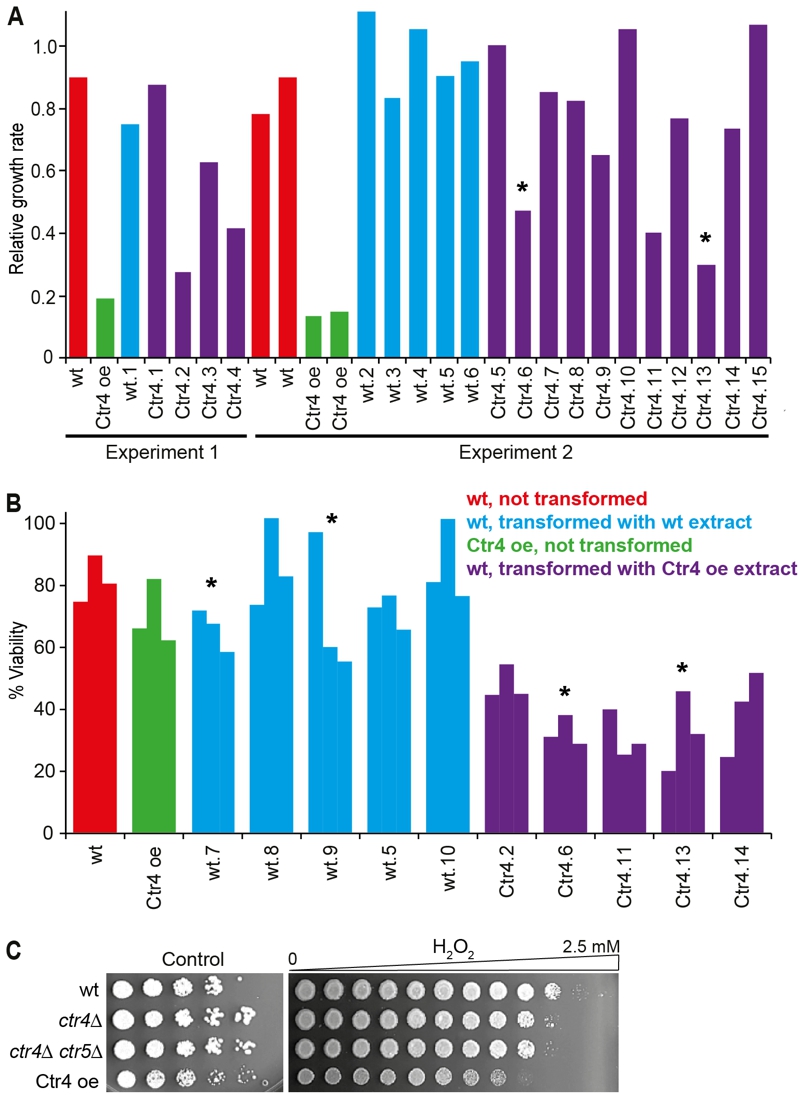
FIGURE 4: Ctr4 overexpression leads to H2O2 sensitivity which is transmissible by protein transformation.
(A) Left, Experiment 1: wild-type cells were transformed with a cell-free extract from wild-type (wt.1) and Ctr4 overexpressing cells (Ctr4.1-Ctr4.4). For all strains, the ratios of maximum growth rate in liquid medium with 1 mM H2O2, relative to maximum growth rate in untreated medium, were determined in a Biolector microfermentor. Data for control wt and Ctr4 overexpression (Ctr4 oe) cells are also shown. Right, Experiment 2: as Experiment 1, but showing additional, independent transformants with extracts from wild-type (wt.2-wt.6) and Ctr4 overexpressing cells (Ctr4.5-Ctr4.15). Data for two independent wild-type control (wt) and two independent Ctr4 overexpression (Ctr4 oe) cells are also shown. Strains whose extracts were used for the protein transformations in the meiosis experiments (Figure 5) are indicated with asterisks.
(B) Wild-type cells were transformed with extracts from wild-type (wt.5, wt.7-wt.10) or Ctr4 overexpressing cells (Ctr4.2. Ctr4.6, Ctr4.11, Ctr4.13, Ctr4.14). Cell viability after treatment with 0.5 mM H2O2 relative to untreated cells was determined for the transformed strains and for control wt and Ctr4 overexpression (Ctr4 oe) strains. Strains whose extracts were used for the protein transformations in the meiosis experiments (Figure 5) are indicated with asterisks.
(C) Wild-type (wt), ctr4Δ single and ctr4Δ ctr5Δ double mutants, and Ctr4 overexpressing cells were spotted in serial dilutions on EMM plates (Control, left) or in equal quantities onto EMM plates containing a gradient of 0 to 2.5 mM H2O2 (right).