Back to article: Inhibitors of glycosomal protein import provide new leads against trypanosomiasis
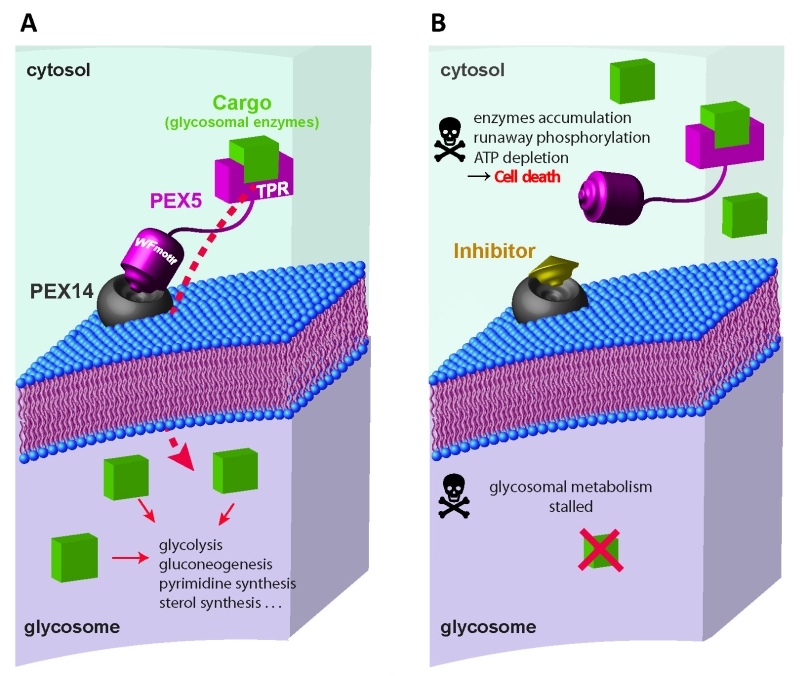
FIGURE 1: Glycosomal protein import as drug target. (A) Glycosomal enzymes synthesized in the cyto-sol are recognized by receptors PEX5 or PEX7, and targeted to gly-cosomes. C-terminal region of PEX5 contains tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domains which recognize the cargo proteins contain-ing PTS1 signal. The cargo-loaded receptor docks at the glycosomal membrane through interaction of PEX5 with PEX14. N-terminal region of PEX5 contains diaromatic pentapeptide motifs (WxxxF/Y), which bind to N-terminal domain of PEX14. This interaction forms a transient pore in the glycosomal membrane that allows import of the enzymes into the glycosomal lumen. (B) The inhibitors of PEX5-PEX14 interaction disrupt glycosomal protein import and mislocalise glycosomal enzymes into the cytosol. Un-controlled activities of the mislocalised glycolytic enzymes cause runaway glucose phosphorylation which accumulates glucose me-tabolites to toxic levels, depletes cellular ATP levels and the meta-bolic imbalance kills the parasite.