Back to article: The cytosolic glyoxalases of Plasmodium falciparum are dispensable during asexual blood-stage development
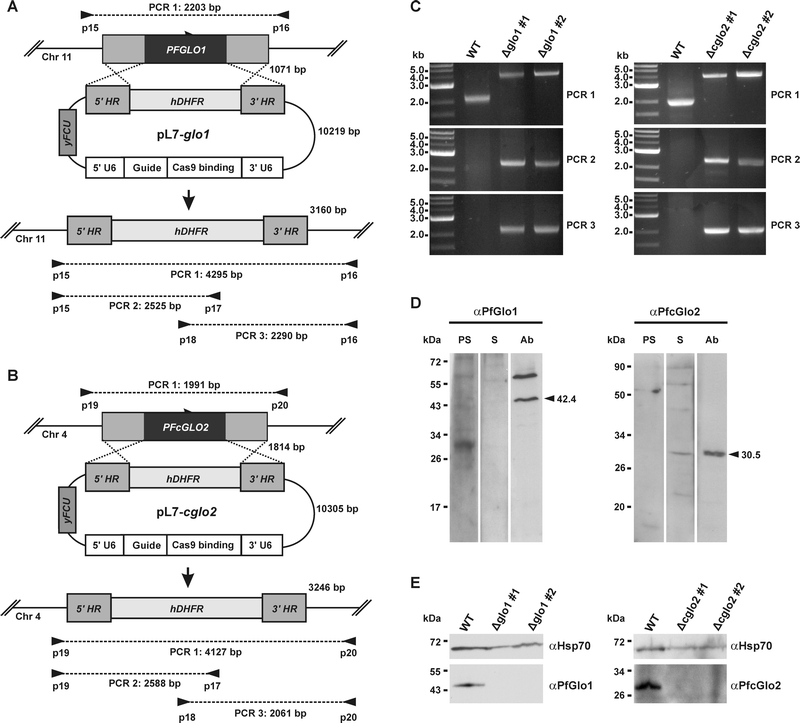
FIGURE 1: Generation and validation of P. falciparum 3D7Δglo1 and 3D7Δcglo2 knockout strains. (A) and (B) Knockout strategy for PFGLO1 and PFcGLO2 using the CRISPR-Cas9 system based on the method by Ghorbal et al. [29]. Primer pairs and expected PCR products 1-3 for wild-type strain 3D7 and knockout parasite lines are indicated. (C) PCR controls with isolated genomic DNA from clonal parasite lines 3D7Δglo1 and 3D7Δcglo2 after transfection, selection and limited dilution. PCR products 1-3 are shown for two clones (#1 and #2) from each knockout experiment. Wild-type strain 3D7 served as a control. (D) Analysis of rabbit peptide antibodies against PfGlo1 and PfcGlo2. P. falciparum extracts from 2 x 107 cells were loaded per lane on a 15% gel, separated by reducing SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting. The expected sizes of PfGlo1 and PfcGlo2 are indicated by arrowheads. PS, S, Ab: Decoration with pre-immune serum, serum and affinity-purified antibody, respectively. (E) Western blot controls with extracts from wild-type strain 3D7 as well as two clonal 3D7Δglo1 and 3D7Δcglo2 parasite lines from panel C using the purified antibodies from panel D. Decoration with an antibody against Hsp70 served as a loading control.
29. Ghorbal M, Gorman M, Macpherson CR, Martins RM, Scherf A, Lopez-Rubio JJ (2014). Genome editing in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Biotechnol 32(8): 819-821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2925