Back to article: VAMP8 mucin exocytosis attenuates intestinal pathogenesis by Entamoeba histolytica
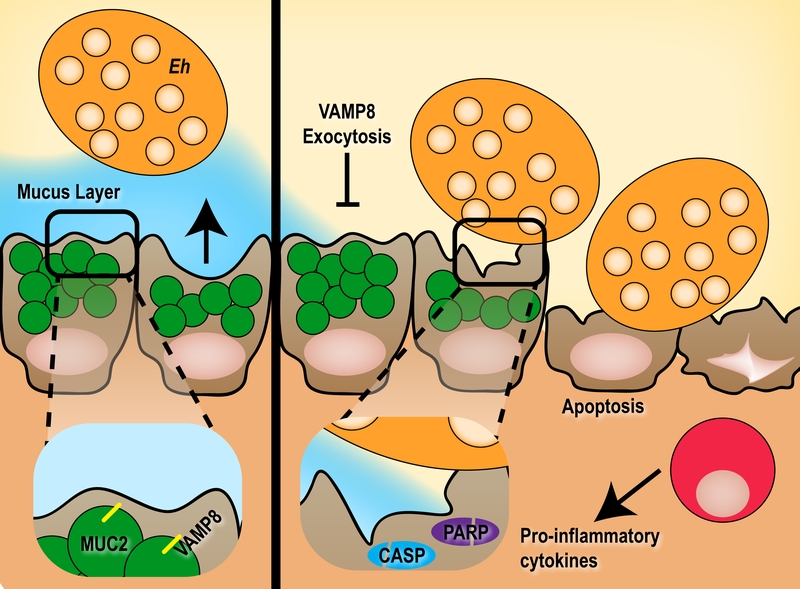
FIGURE 1: The pathogenesis of E. histolytica in the absence of VAMP8-mucin exocyto-sis. Under normal conditions (left), E. histolytica (Eh) colonizes the mucus layer and induce VAMP8-dependent mucin exocytosis when in close proximity to goblet cells. This hyper secretion of mucin is essential in restricting pathogen contact with the epithelium in a normal host-pathogen relationship. However, if mucin exocytosis is blocked through VAMP8 deficiency (right), the host cannot adequately fend off the parasite leading to direct contact with mucosal epithelial cells and induction of apoptosis through caspase 3, 9 and PARP cleavage evoking an acute pro-inflammatory response in disease pathogenesis.