Back to article: Mitochondrial energy metabolism is required for lifespan extension by the spastic paraplegia-associated protein spartin
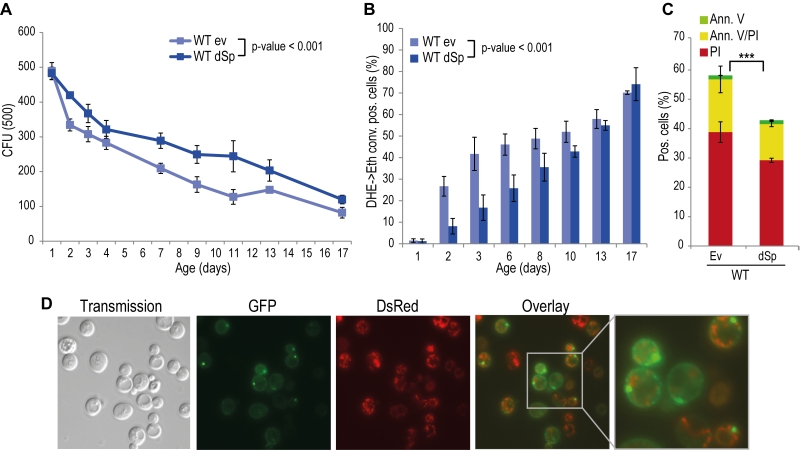
FIGURE 1: Spartin exerts a pro survival function in yeast. (A) Survival during chronological aging of WT cells expressing Drosophila spartin (dSp) or cells harboring the corresponding empty vector control (ev). Yeast cells were evaluated for clonogenicity at indicated time points after induction of expression by shift to 2% galactose containing media. Data represent mean values of at least four independent experiments performed at the same time. CFU, colony-forming unit. Error bars represent standard error of mean (SEM). (B) Quantification of oxidative stress levels (by conversion of dihydroethidium (DHE) to ethidium (Eth)). (C) phosphatidylserine externalization (apoptotic cell death) and loss of membrane integrity (necrotic cell death) using annexin V/propidium iodide (Ann.V/PI) costaining and flow cytometry-assisted quantification. (D) Fluorescence microscopy of WT cells expressing dSpEGFP (green) and mitochondria visualized by co-expression with DsRed fused to a mitochondrial localization sequence on day 1 of chronological aging.