Back to article: Production of poly-β-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine by MatAB is required for hyphal aggregation and hydrophilic surface adhesion by Streptomyces
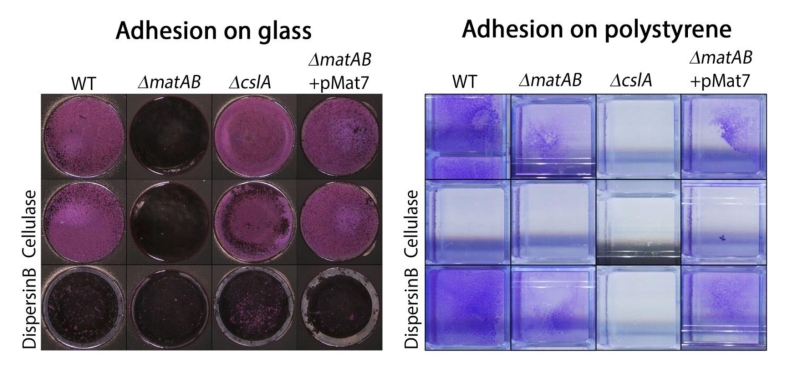
FIGURE 6: Adhesion assays visualizing EPS-mediated attachment to glass and polystyrene. Attachment of S. lividans 66 to glass was antagonized by treatment with dispersin B (50 µg/ml) or by deletion of matAB, while addition of cellulase (0.2 U/ml) or deletion of cslA had no effect. The opposite was seen for attachment to polystyrene, which was antagonized by cellulase or by deletion of cslA and not by dispersin B or deletion of matAB. The ability to attach to glass was restored to matAB mutants by the introduction of plasmid pMAT7.