Back to article: Microbial competition between Escherichia coli and Candida albicans reveals a soluble fungicidal factor
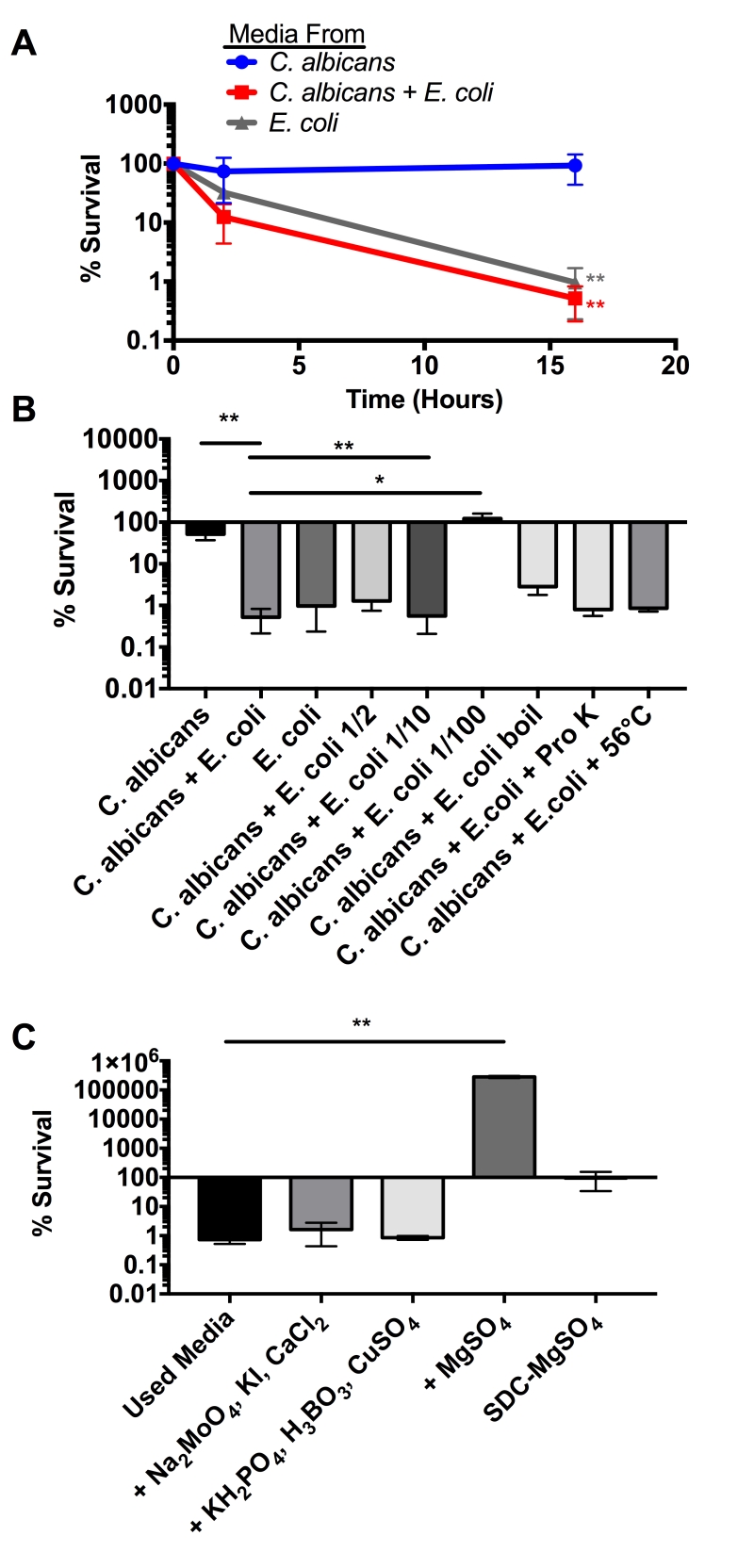
FIGURE 2: E. coli produces a soluble fungicidal molecule. (A) Percent survival of C. albicans cultured in the indicated conditioned media collected after 6 hours of co-culture. Statistical significance was calculated using an unpaired two-tailed t-test in which the E. coli and the C. albicans + E. coli medias were compared to the C. albicans media control. (B) Percent survival of C. albicans cultured in the indicated conditioned media for 16 hours. Statistical significance was calculated using a one-way ANOVA in Prism 7.0. P-values were subsequently corrected for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni method. All conditions were compared to the C. albicans media control. (C) Percent survival of C. albicans cultured in E. coli + C. albicans conditioned media for 16 hours. Compounds were added at the concentrations consistent with standard YNB [Boric acid (0.5 mg/L), Copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate (0.04 mg/L) Sodium molybdate (0.2 mg/L), Potassium iodide (0.1 mg/L), Calcium chloride dihydrate (100 mg/L), Potassium phosphate monobasic anhydrous (1000 mg/L) and Magnesium sulfate anhydrous (500 mg/L)]. Statistical significance was calculated using a one-way ANOVA in Prism 7.0 to compare all conditions to the used media control. P-values were subsequently corrected for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni method. Statistical significance is shown (*p > 0.05; **p > 0.01 ***p > 0.001).