Back to article: Snf1 cooperates with the CWI MAPK pathway to mediate the degradation of Med13 following oxidative stress
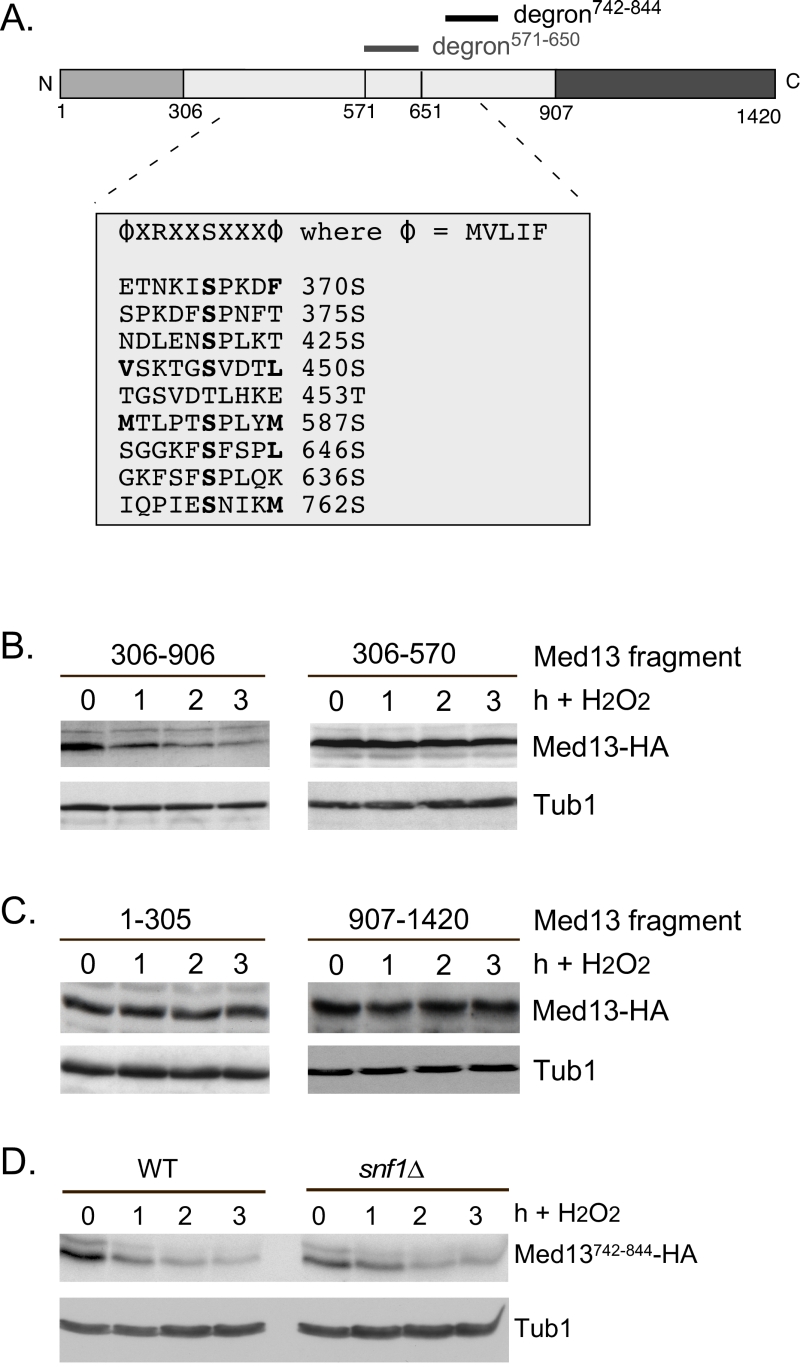
FIGURE 6: Other potential Snf1 sites in Med13 are not required for its degradation following H2O2 stress. (A) Map of Med13 outlying the positions of the two Med13 degrons, the consensus Snf1 target site [58] and potential Snf1 sites, identified by published proteomic screens. (B) and (C) Wild-type (RSY10) cultures harboring the NLS-Med13-HA constructs shown were grown to mid-log phase (0 h) then treated with 0.4 mM H2O2 for the indicated times. Med13-HA levels were determined by Western blot analysis. Tub1 levels were used as a loading control. (D) Mid-log wild type or snf1∆ cultures (RSY202) harboring HA tagged Med13 degron742-844 (pDS32) were subjected to an H2O2 timecourse experiment and protein extracts analyzed by Western blot. Tub1 levels were used as loading controls.
58. Dale S, Wilson WA, Edelman AM, Hardie DG (1995). Similar substrate recognition motifs for mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase, higher plant HMG-CoA reductase kinase-A, yeast SNF1, and mammalian calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. FEBS Lett 361(2-3): 191-195. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)00172-6