Back to article: Specific mutations in the permease domain of septal protein SepJ differentially affect functions related to multicellularity in the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena
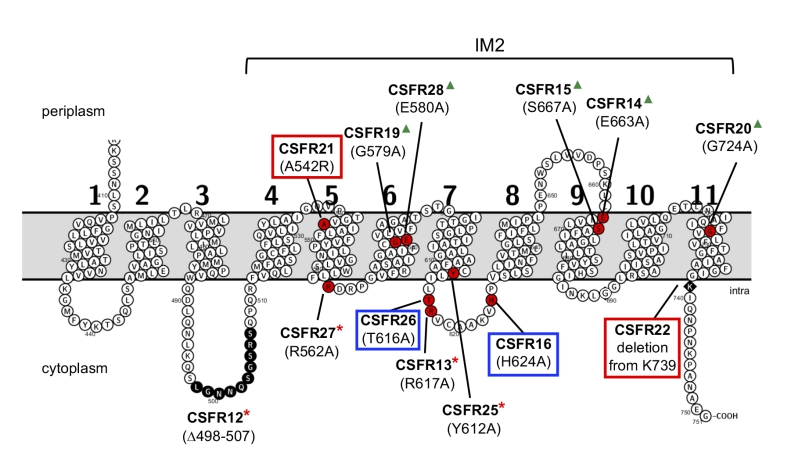
FIGURE 2: Schematic of the permease domain of SepJ from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 indicating the mutations introduced in this work. Transmembrane segments are numbered 1 to 11 according to the prediction of the TMHMM program. The last eight TMSs are strongly conserved in SepJ proteins constituting subdomain IM2 (see Fig. S1). Because there is strong evidence for a cytoplasmic C-terminus [18, 27], the showed topology is very likely to be correct for subdomain IM2. Red circles, individual amino acids mutated; black circles, residues deleted in strain CSFR12; black rhomboid, residue at which a C-terminal deletion started. Group 1 mutations are framed in red; group 2 mutations are framed in blue; group 3 mutations are indicated by red asterisks; group 4 mutations are indicated by green triangles.
18. Flores E, Pernil R, Muro-Pastor AM, Mariscal V, Maldener I, Lechno-Yossef S, Fan Q, Wolk CP, Herrero A (2007). Septum-localized protein required for filament integrity and diazotrophy in the heterocyst-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol 189(10): 3884-3890. http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jb.00085-07
27. Ramos-León F, Mariscal V, Frías JE, Flores E, Herrero A (2015). Divisome-dependent subcellular localization of cell-cell joining protein SepJ in the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena. Mol Microbiol 96(3): 566-580. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/10.1111/mmi.12956