Back to article: Bacterial pathogens under high-tension: Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to von Willebrand factor is activated by force
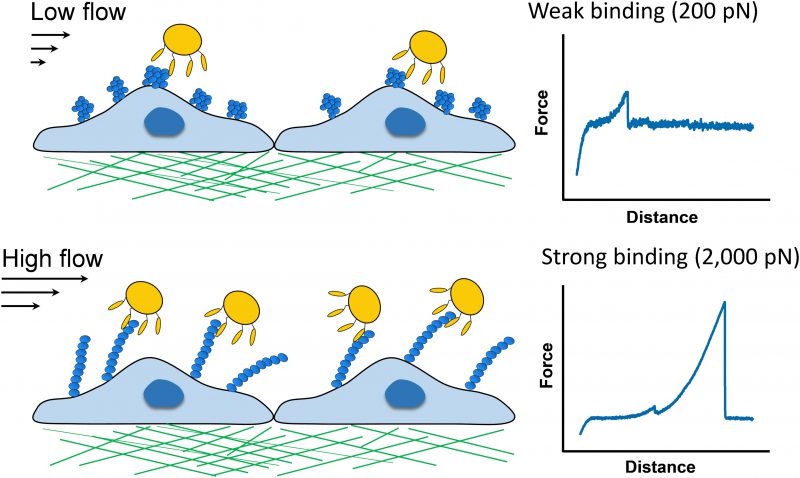
FIGURE 1: Force-induced activation of the SpA-vWF bond. Single-molecule pulling experiments led us to propose a mechanism whereby force-induced extension of vWF leads to the exposure of a cryptic binding site to which SpA proteins on the bacterial cell surface strongly bind. SpA-vWF bonds at high stress are much stronger (binding strength of ~2,000 pN) than most receptor-ligand bonds measured to date, thus highlighting the importance of protein mechanobiology in bacterial adhesion.