Back to article: Regulation of anti-microbial autophagy by factors of the complement system
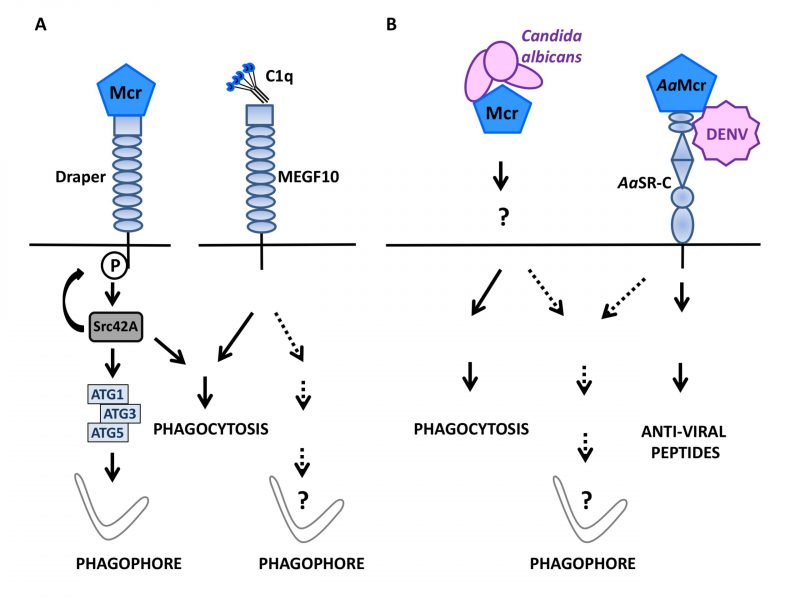
FIGURE 2: Macroglobulin complement related factor (Mcr) in antimicrobial defense and autophagy.(A) During D. melanogaster development, the complement-like opsonin Macroglobulin complement related/TEPVI (Mcr), that is highly similar to mammalian complement factor C3, can initiate autophagy in both epithelial cells and macrophages by engaging Draper, a Src42A protein kinase-coupled, EGF-like-repeat-containing receptor known to signal for phagocytosis (left). Whether Multiple EGF-like-domain Factor 10 (MEGF10), a mammalian ortholog of Draper that mediates phagocytosis in response to C1q binding, can also signal for autophagy induction is unknown (right). (B) Mcr mediates the selective phagocytosis of Candida albicans in D. melanogaster (left) and, along with the scavenger receptor-C (AaSR-C) is involved in initiating the production of anti-viral peptides in response to the Dengue virus (DENV) in Aedes aegypti (AaMcr)(right). Whether pathogen sensing by Mcr (with a role for Draper in the case of D. melanogaster?) can activate anti-microbial autophagy in insects remains to be studied.