Back to article: Histone H3E73Q and H4E53A mutations cause recombinogenic DNA damage
image description
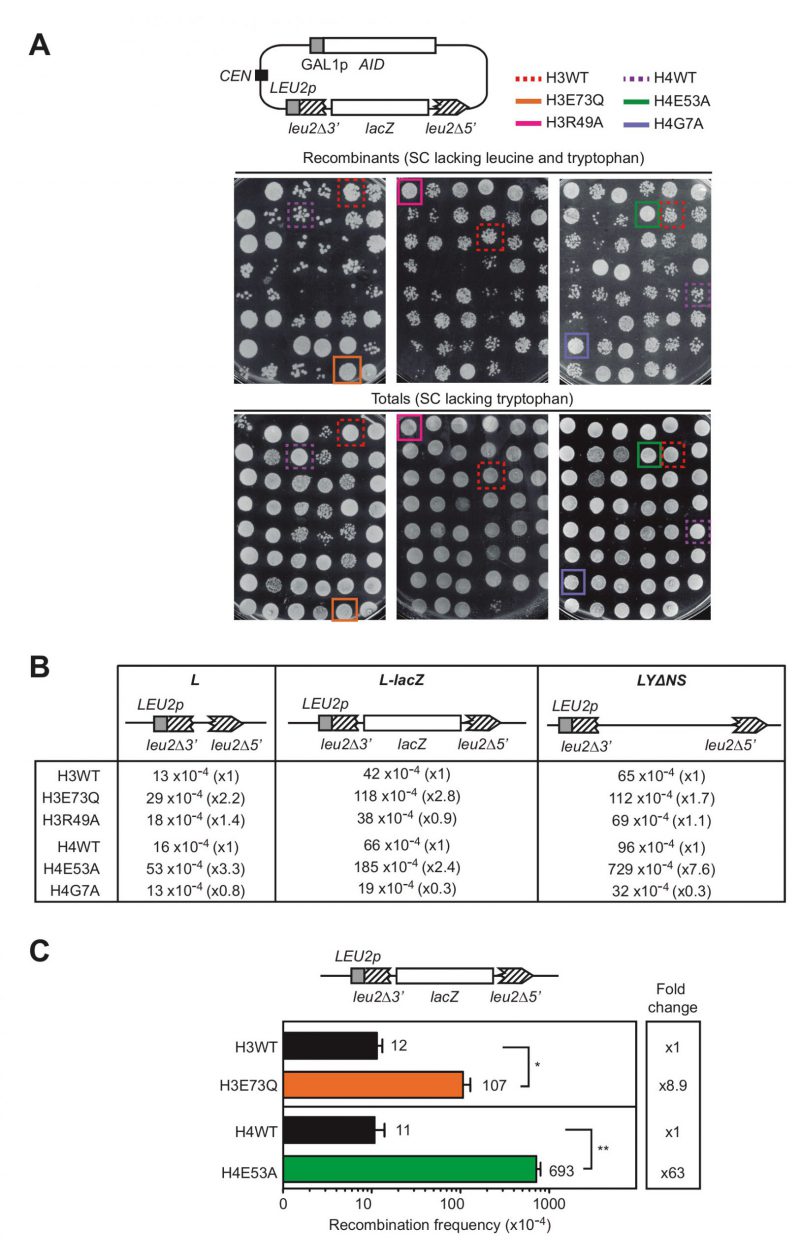
FIGURE 1: Histone H3E73Q and H4E53A mutants cause a hyper-recombination phenotype.(A) A scheme of the pLZGAID plasmid is shown. Visual analysis of direct-repeat recombination frequencies after AID overexpression in WT and histone mutant strains from the collection [8] transformed with pLZGAID. Similar dilutions of cultures grown in galactose media in 96-well-plates were plated in SC lacking leucine and tryptophan to detect Leu+ colonies (Recombinants) and in SC lacking tryptophan to visualize the total cells (Totals) and incubated for 3 days. Wild-type (H3WT), H3E73Q (H3E73Q), H3R49A (H3R49A), H4 wild-type (H4WT), H4E53A (H4E53A) and H4G7A (H4G7A) strains are pointed out. (B) A scheme of the L, L-lacZ, and LYΔNS direct-repeat recombination system is shown. Analysis of median direct-repeat recombination frequencies in random colonies from H3 wild-type (H3WT), H3E73Q (H3E73Q), H3R49A (H3R49A), H4 wild-type (H4WT), H4E53A (H4E53A) and H4G7A (H4G7A) strains transformed with pRS316-L, pSCH204, and pRS316-LYΔNS respectively. (C) A scheme of the L-lacZ direct-repeat recombination system is shown. Analysis of direct-repeat recombination frequencies in H3 wild-type (H3WT), H3E73Q (H3E73Q), H4 wild-type (H4WT) and H4E53A (H4E53A) strains transformed with pSCH204 (n = 3). Means and SEM are plotted. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01 (two-tailed Student's t-test).
8. Dai J, Hyland EM, Yuan DS, Huang H, Bader JS, Boeke JD (2008). Probing nucleosome function: a highly versatile library of synthetic histone H3 and H4 mutants. Cell 134(6): 1066-1078. 10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.019