Back to article: Histone H3E73Q and H4E53A mutations cause recombinogenic DNA damage
image description
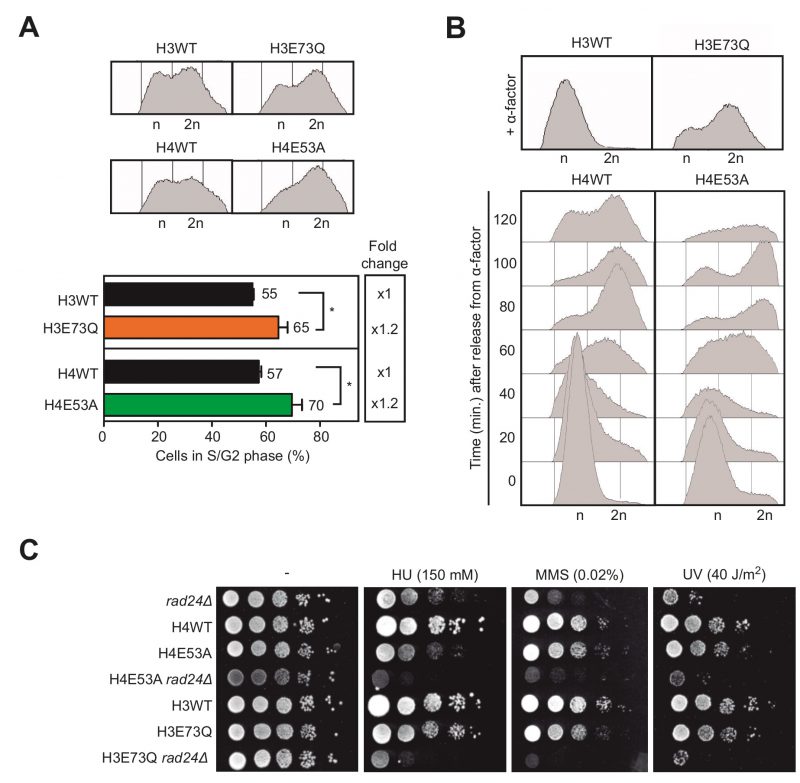
FIGURE 4: Histone H3E73Q and H4E53A mutants increase replication stress.(A) Analysis and quantification of cell cycle phases in asynchronous cultures of H3 wild-type (H3WT), H3E73Q (H3E73Q), H4 wild-type (H4WT) and H4E53A (H4E53A) strains by FACS (n=3). (B) Analysis of cell cycle progression in H3 wild-type (H3WT), H3E73Q (H3E73Q), H4 wild-type (H4WT) and H4E53A (H4E53A) strains by FACS. (C) Sensitivity to HU (150 mM), MMS (0.02%), UV (40 J/m2) of rad24Δ (R24), H3 wild-type (H3WTn), H3E73Q (H3E73Qn), H3E73Q rad24Δ (E73QR24), H4 wild-type (H4WTn), H4E53A (H4E53An) and H3E73Q rad24Δ (E53AR24) strains coming from a crossing H3E73Q and H4E53A with W303-1B rad24Δ. Similar results were obtained with different spores from the same genetic cross. Means and SEM are plotted in (A). *p ≤ 0.05. (two-tailed Student's t-test).