Back to article: Multiple genome analysis of Candida glabrata clinical isolates renders new insights into genetic diversity and drug resistance determinants
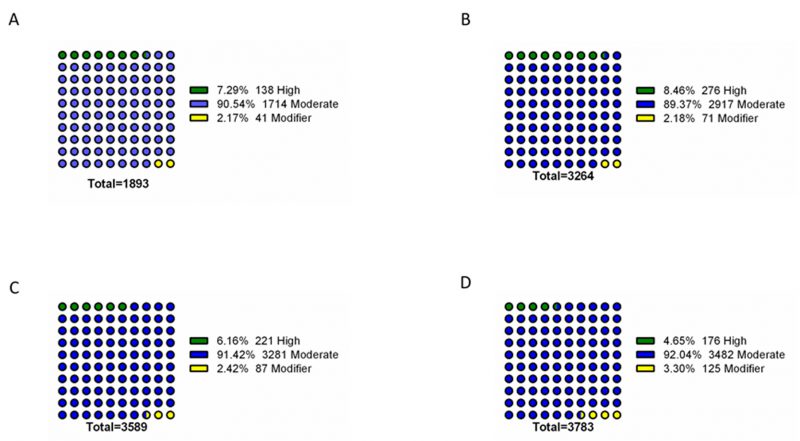
FIGURE 2: Impact analysis of genomic variants found exclusively in the genomes of resistant isolates. The assessed mutations are present in the genomes of azole resistant (A), echinocandin intermediate (B), echinocandin resistant (C) and multi resistant (D) isolates, being absent from the genomes of susceptible isolates. For each resistance group, the catalogued mutations are specific to that group. Variant impact was predicted with SnpEff [10]: High – the variant is assumed to have high (disruptive) impact in the protein, probably causing protein truncation, loss of function or triggering nonsense mediated decay; Moderate – A non-disruptive variant that might change protein effectiveness; Modifier – usually non-coding variants or variants affecting non-coding genes, where predictions are difficult or there is no evidence of impact.
10. Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang LL, Coon M, Nguyen T, Wang L, Land SJ, Lu X, and Ruden DM (2012). A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 6(2): 80. 10.4161/FLY.19695