Back to article: The role of invariant surface glycoprotein 75 in xenobiotic acquisition by African trypanosomes
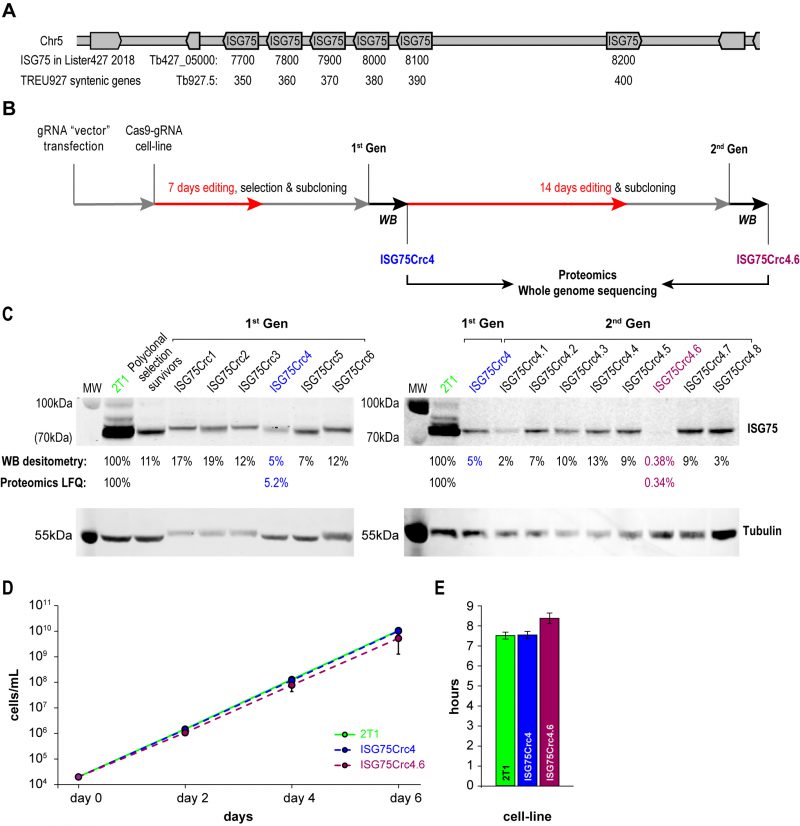
FIGURE 2: CRISPR-Cas9 strategy for obtaining ISG75 knockout. (A) ISG75 locus map in T. brucei Lister 427. (B) Following delivery and selection for cells stably expressing a chosen gRNA, Cas9 was induced for 7 days and the population selected with suramin (70µm) for 4 days, then subcloned and individual clones subjected to Western blot analysis (WB) (in C). Clone 4 termed ISG75Crc4 and expressing ∼5% of ISG75 parental levels was subjected to an additional 14 days of Cas9 induction, subcloned again and individual clones again subjected to Western blot analysis. Clones ISG75Crc4 and ISG75Crc4.6 were analysed by whole genome sequencing and proteomics to assess respectively the genomic architecture of the edited ISG75 locus and remaining protein levels. (C) Western blot and proteomics analysis of first- and second-generation clones reveals ISG75Crc4 and ISG75Crc4.6 as 95% knockdown and effective knockout clones respectively. Numbers given are Western blot densitometry values for 1st and 2nd-generation clones and proteomics label free quantification for clones ISG75Crc4 and ISG75Crc4.6. (D) Cumulative growth curves over six days of cultivation for parental 2T1 (green), mutant ISG75Crc4 (blue) and ISG75Crc4.6 (purple) cell-lines. Three replicates for each line were grown in parallel. Error bars, standard deviations. (E) Average doubling times for 2T1, ISG75Crc4 and ISG75Crc4.6, calculated from (D).