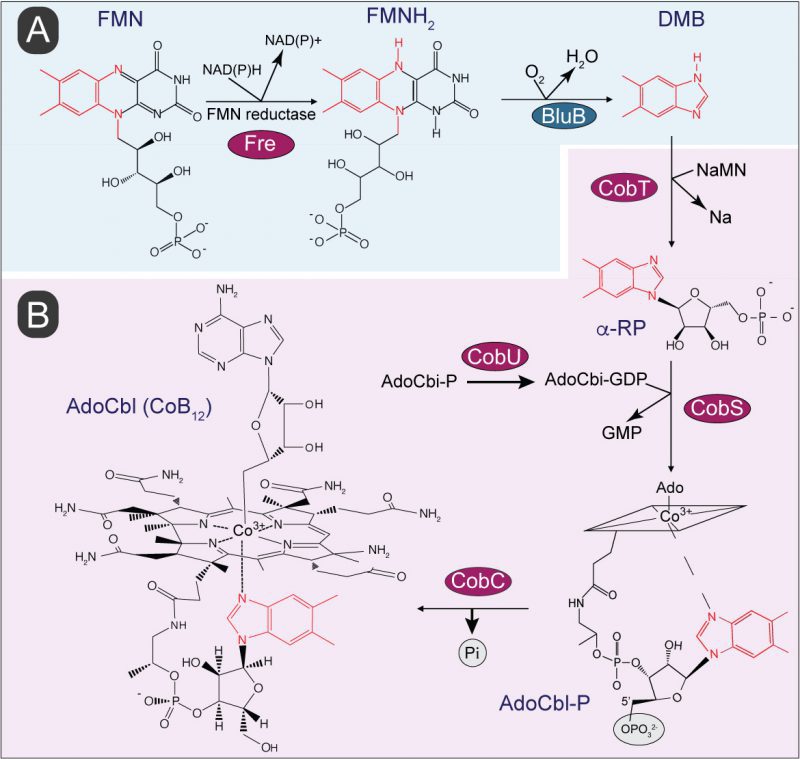
FIGURE 1: Biosynthesis of 5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) and its incorporation into coenzyme B12 (CoB12). (A) Aerobic pathway of DMB biosynthesis involves oxidative fragmentation of reduced flavin mononucleotide (FMNH2) by DMB synthase, BluB. Atoms of the isoalloxazine ring and ribityl tail of FMNH2 converted into DMB are shown in red. (B) In S. Typhimurium incorporation of DMB into CoB12 is initiated by its activation into the alpha ribotide, α-ribazole-5′-phosphate (α-RP) followed by condensation of activated intermediates and dephosphorylation to yield biologically active CoB12. Abbreviations: FMN, flavin mononucleotide; NAD(P), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate); NaMN, nicotinate mononucleotide; Na, nicotinate; AdoCbi-GDP, adenosylcobinamide- guanosine diphosphate. GMP, guanosine monophosphate; AdoCbl-P, adenosylcobalamin-phosphate; AdoCbl, adenosylcobalamin; CobT, NaMN:DMB phosphoribosyltransferase; CobS, AdoCbl-5' phosphate synthase; CobC, adenosylcobalamin phosphatase; Fre, NAD(P)H:flavin reductase. Enzyme homologs presence in S. Typhimurium are shown in red circles. The rhomboid structure with the Co3+ ion in the middle is a cartoon of the complex cyclic tetrapyrrole ring shown at the end of the pathway.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.