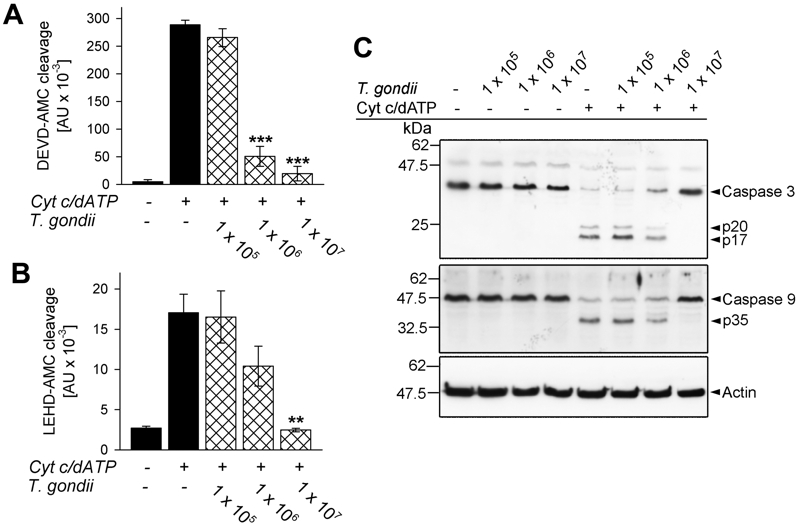
FIGURE 1: T. gondii inhibits cytochrome c-induced activation of the caspase 9-caspase3/7 cascade in cell-free cytosolic extracts.
(A, B) Cell-free cytosolic extracts of Jurkat cells were incubated with increasing amounts of parasites as indicated (cross-hatched bars; no. of parasites per 0.1 ml) or were left untreated (black bars). After 1 hour, caspase activation was triggered or not by cytochrome c and dATP. Cleavage of the caspase 3/7 substrate DEVD-AMC (A) or of the caspase 9 substrate LEHD-AMC (B) was measured fluorimetrically. Data represent the increase in substrate cleavage over time; they represent means ± S.E.M. from at least 3 independent experiments. Significant differences were identified by Student’s t-test (** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001).
(C) Cell-free cytosolic extracts incubated or not with T. gondii as indicated and incubated or not with cytochrome c/dATP to trigger caspase activation were resolved by SDS-PAGE. After protein transfer to nitrocellulose, membranes were probed with antibodies recognizing caspase 3, caspase 9 and actin. Immune complexes were visualized using peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies and enhanced chemiluminescence detection. The experiment was repeated once with similar results.