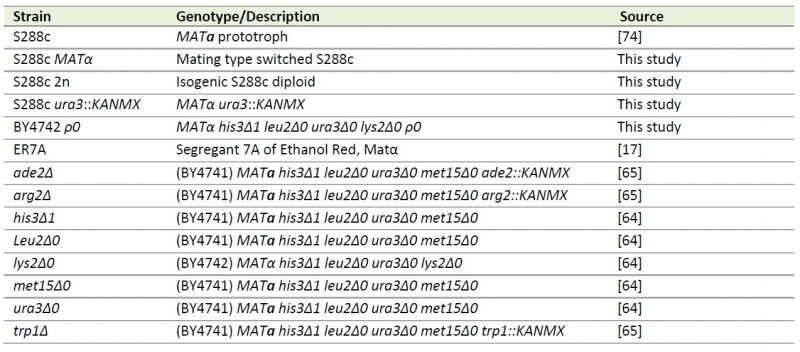
TABLE 2. S. cerevisiae strains used in this study.
17. Hubmann G, Foulquie-Moreno MR, Nevoigt E, Duitama J, Meurens N, Pais TM, Mathe L, Saerens S, Nguyen HT, Swinnen S, Verstrepen KJ, Concilio L, de Troostembergh JC, Thevelein JM (2013). Quantitative trait analysis of yeast biodiversity yields novel gene tools for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 17: 68-81. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.02.006
64. Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD (1998). Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14(2): 115-132.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/%28SICI%291097-0061%2819980130%2914:2%3C115::AID-YEA204%3E3.0.CO;2-2/abstract
65. Winzeler EA, Shoemaker DD, Astromoff A, Liang H, Anderson K, Andre B, Bangham R, Benito R, Boeke JD, Bussey H, Chu AM, Connelly C, Davis K, Dietrich F, Dow SW, El Bakkoury M, Foury F, Friend SH, Gentalen E, Giaever G, Hegemann JH, Jones T, Laub M, Liao H, Liebundguth N, Lockhart DJ, Lucau-Danila A, Lussier M, M’Rabet N, Menard P, et al. (1999). Functional characterization of the S. cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285(5429): 901-906. http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5429.901