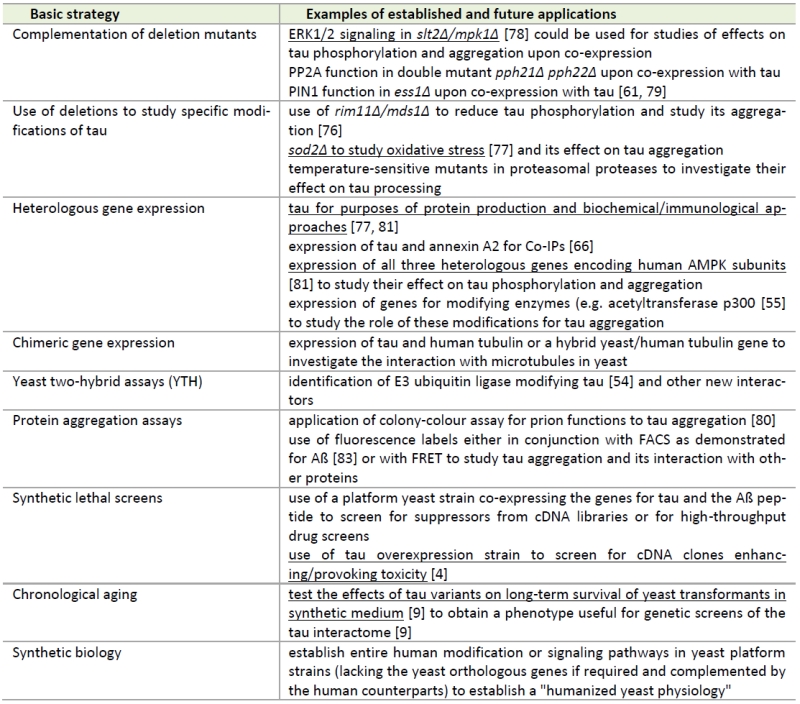
TABLE 1. Basic approaches to study aspects of tau biology in S. cerevisiae*
* aspects also applicable to the alternative non-conventional yeast K. lactis (but not yet examined for tau-related functions) are underlined. Approaches without references are either unpublished results from our laboratory or suggestions for future investigations (see text for details).
4. Verduyckt M, Vignaud H, Bynens T, Van den Brande J, Franssens V, Cullin C, Winderickx J (2016). Yeast as a Model for Alzheimer’s Disease: Latest Studies and Advanced Strategies. Methods Mol Biol 1303:197-215. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2627-5_11
9. De Vos A, Anandhakumar J, Van den Brande J, Verduyckt M, Franssens V, Winderickx J, Swinnen E (2011). Yeast as a model system to study tau biology. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:428970. http://dx.doi.org/10.4061/2011/428970
54. Flach K, Ramminger E, Hilbrich I, Arsalan-Werner A, Albrecht F, Herrmann L, Goedert M, Arendt T, Holzer M (2014). Axotrophin/MARCH7 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and ubiquitinates tau protein in vitro impairing microtubule binding. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(9): 1527-1538. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.05.029
55. SMin SW, Chen X, Tracy TE, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang C, Shirakawa K, Minami SS, Defensor E, Mok SA, Sohn PD, Schilling B, Cong X, Ellerby L, Gibson BW, Johnson J, Krogan N, Shamloo M, Gestwicki J, Masliah E, Verdin E, Gan L (2015). Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits. Nat Med 21(10): 1154-1162. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2014.04.102
61. De Vos A, Bynens T, Rosseels J, Coun C, Ring J, Madeo F, Galas MC, Winderickx J, Franssens V (2015). The peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase Pin1/Ess1 inhibits phosphorylation and toxicity of tau in a yeast model for Alzheimer’s disease. AIMS Molecular Science 2(2): 144-160. http://dx.doi.org/10.3934/molsci.2015.2.144
66. Gauthier-Kemper A, Weissmann C, Golovyashkina N, Sebo-Lemke Z, Drewes G, Gerke V, Heinisch JJ, Brandt R (2011). The frontotemporal dementia mutation R406W blocks tau’s interaction with the membrane in an annexin A2-dependent manner. J Cell Biol 192(4): 647-661. http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201007161
76. Vandebroek T, Terwel D, Vanhelmont T, Gysemans M, Van Haesendonck C, Engelborghs Y, Winderickx J, Van Leuven F (2006). Microtubule binding and clustering of human Tau-4R and Tau-P301L proteins isolated from yeast deficient in orthologues of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta or cdk5. J Biol Chem 281(35): 25388-25397. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m602792200
77. Vanhelmont T, Vandebroek T, De Vos A, Terwel D, Lemaire K, Anandhakumar J, Franssens V, Swinnen E, Van Leuven F, Winderickx J (2010). Serine-409 phosphorylation and oxidative damage define aggregation of human protein tau in yeast. FEMS Yeast Res 10(8): 992-1005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2010.00662.x
78. Levin-Salomon V, Maayan I, Avrahami-Moyal L, Marbach I, Livnah O, Engelberg D (2009). When expressed in yeast, mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinases lose proper regulation and become spontaneously phosphorylated. Biochem J 417(1): 331-340. http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/bj20081335
79. Bailey ML, Shilton BH, Brandl CJ, Litchfield DW (2008). The dual histidine motif in the active site of Pin1 has a structural rather than catalytic role. Biochemistry 47(44): 11481-11489. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi800964q
80. Tenreiro S, Munder MC, Alberti S, Outeiro TF (2013). Harnessing the power of yeast to unravel the molecular basis of neurodegeneration. J Neurochem 127(4): 438-452. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12271
81. Ye T, Bendrioua L, Carmena D, Garcia-Salcedo R, Dahl P, Carling D, Hohmann S (2014). The mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase complex mediates glucose regulation of gene expression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 588(12): 2070-2077. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.039
82. Rosseels J, Van den Brande J, Violet M, Jacobs D, Grognet P, Lopez J, Huvent I, Caldara M, Swinnen E, Papegaey A, Caillierez R, Buee-Scherrer V, Engelborghs S, Lippens G, Colin M, Buee L, Galas MC, Vanmechelen E, Winderickx J (2015). Tau monoclonal antibody generation based on humanized yeast models: impact on Tau oligomerization and diagnostics. J Biol Chem 290(7): 4059-4074. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m114.627919
83. Caine J, Sankovich S, Antony H, Waddington L, Macreadie P, Varghese J, Macreadie I (2007). Alzheimer’s Abeta fused to green fluorescent protein induces growth stress and a heat shock response. FEMS Yeast Res 7(8): 1230-1236.http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2007.00285.x