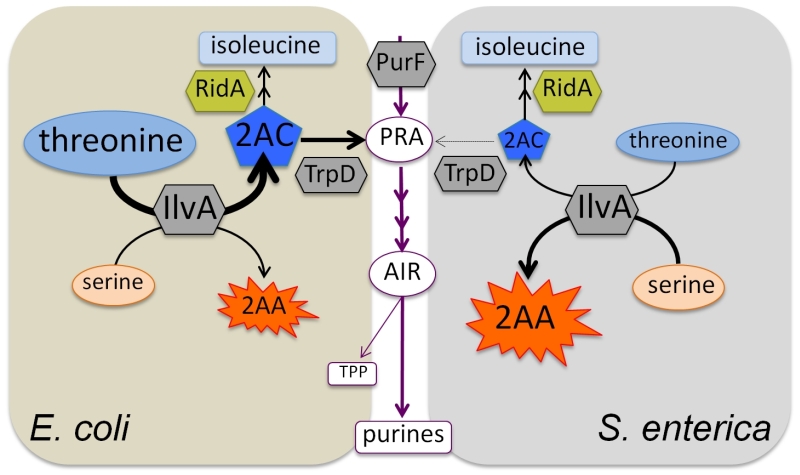
FIGURE 1: S. enterica and E. coli have distinct metabolic network structures surrounding thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) biosynthesis. The metabolic network structures leading to IlvA/TrpD-dependent TPP synthesis in S. enterica and E. coli are shown. Notably, although E. coli and S. enterica have the same enzymes, TPP biosynthesis from threonine is only detectable in E. coli. A working model suggests that relative levels of threonine and serine, the substrates for IlvA, influence the structure and function of the metabolic network. The purine/TPP pathway is shown in maroon with the first enzyme, PurF, and relevant branch metabolites, PRA and AIR, indicated. The thickness of the arrows is meant to represent carbon flux. The two intermediates in the IlvA reaction mechanism, 2-AC and 2-AA are shown. The diversion of 2-AC to PRA formation is allowed by the concentration of threonine available to IlvA in E. coli. In our model, we hypothesize 2-AA from serine is more prevalent than 2-AC in S. enterica, due to the lower level of threonine available for IlvA.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.