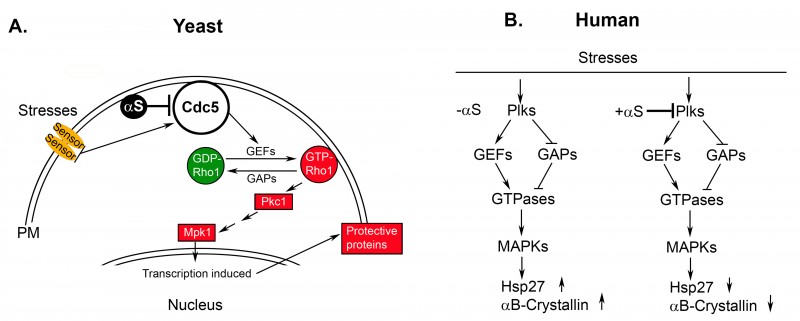
FIGURE 1: α-Syn disrupts cell signaling.
(A) Model for how α-syn disrupts the cell wall integrity pathway in yeast. This pathway is a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway that is similar to the p38 stress-activated pathway in humans.
(B) Model for how α-syn disrupts the p38 stress-activated signaling pathway in humans. In (A) and (B), α-syn inhibits the upstream polo-like kinase if and only if one of the following two conditions is met: (i) α-syn is expressed at high levels or (ii) cells are subjected to high temperatures (> 40°C). If conditions (i) and (ii) are met, then inhibition of stress signaling could be very robust. αS, α-synuclein; GEF, guanine exchange factor; GAP, GTPase-activating protein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mpk1, yeast MAP kinase; Pkc1, yeast protein kinase C; Plks, human polo-like kinase; ↑, indicates increased expression and/or increased activity; ↓, indicates decreased expression and/or decreased activity.