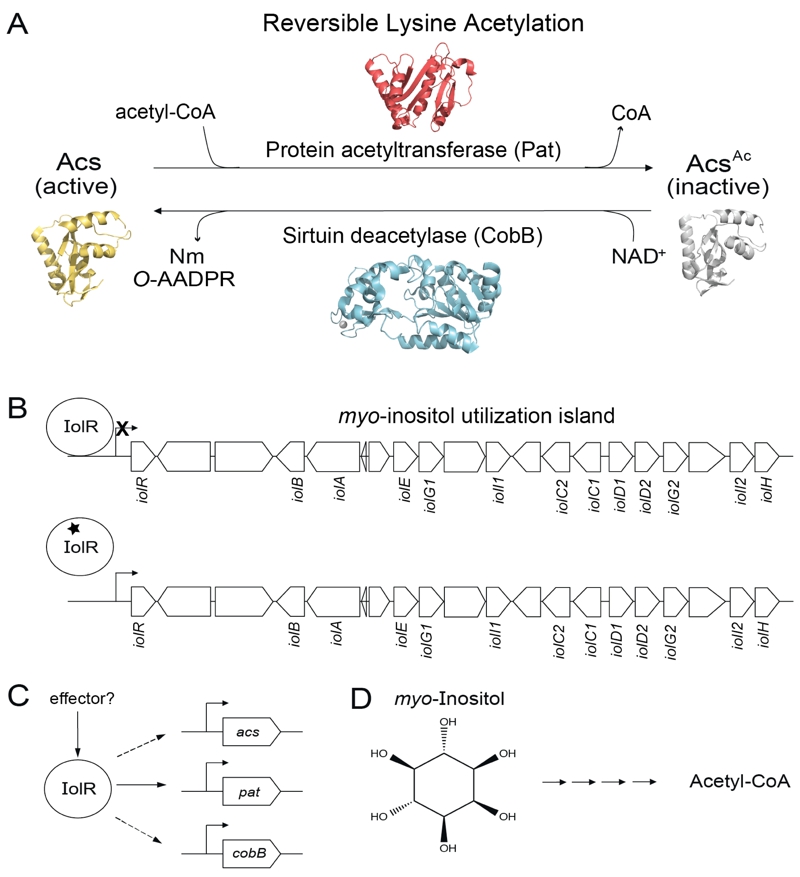
FIGURE 1: IolR activates expression of the reversible lysine acetylation (RLA) system in S. enterica and integrates it with that of its substrate, the acetyl-CoA synthetase, Acs.
(A) In S. enterica, the activity of the AMP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetase (Acs) is post-translationally modified by the protein acetyltransferase, Pat. This modification is reversible by the activity of the NAD+-consuming class III sirtuin deacetylase, CobB, which releases the products O-acetyl-ADP-ribose (O-AADPR) and nicotinamide (Nm).
(B) IolR binds to and represses transcription of the myo-inositol utilization island when myo-inositol is not available. Repression is relieved through binding of 2-deoxy-5-keto-D-gluconic acid 6-phosphate (black star), a product of myo-inositol metabolism, to IolR.
(C) IolR is responsible for activation of expression of pat, acs, and cobB. The identity of a potential effector of this process is unknown.
(D) Structure of myo-inositol, whose degradation leads to the generation of acetyl-CoA.