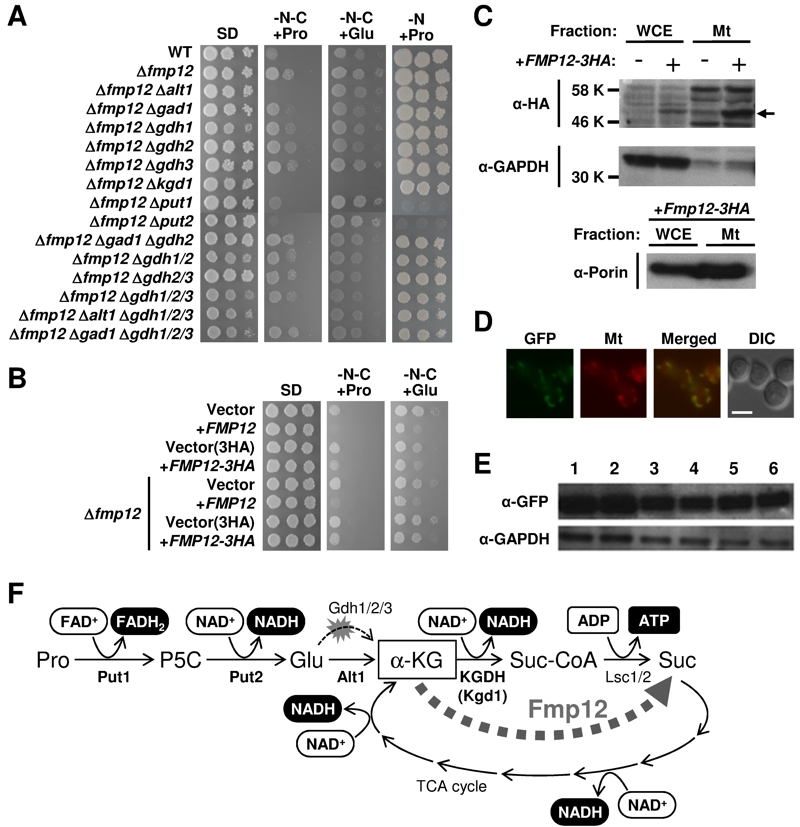
FIGURE 1: Proline/glutamate metabolism as the sole carbon source and its control mediated by Fmp12.
(A) Growth phenotypes of S. cerevisiae wild-type strain (BY4741) and its deletion mutants on SD, SD-N-C+Pro, SD-N-C+Glu, and SD-N+Pro media.
(B) Growth phenotypes of S. cerevisiae BY4741u or BY4741u Δfmp12 cells harboring the empty vector (pVV208, pVV209) or overexpressing FMP12 (pVV208-FMP12, pVV209-FMP12) on SD, SD-N-C+Pro, and SD-N-C+Glu media.
(C) Detection of Fmp12-3HA in the whole cell extract (WCE) and in the mitochondria fraction (Mt). The symbol -/+ indicates the sample from the cells without or with expression of Fmp12-3HA from pVV209-FMP12. The arrow indicates the predicted size of Fmp12-3HA truncated at its amino-terminal MTS. GAPDH and porin were analyzed as controls of cytoplasmic and mitochondrial proteins, respectively.
(D) Subcellular localization of Fmp12-yeGFP by fluorescent microscopy. GFP signals (GFP), MitoTracker signals (Mt), merged signals (Merged), and differential interference contrast images (DIC) are shown. The scale bar represents 5 μm.
(E) Western blot analysis of Fmp12-yeGFP under different nutritional conditions. S. cerevisiae FMP12-yeGFP cells were cultivated on solid media at 30°C for 5 days. The numbers indicate the media as follows: 1: SD, 2: SD+Pro, 3: SD-N-C+Pro, 4: SD-C+Pro, 5: SD-N-C+Glu, 6: SD-C+Glu. GAPDH was used as a protein-loading control.
(F) Energy production by proline metabolism as the sole carbon source in S. cerevisiae. Pro: proline, P5C: Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate, Glu: glutamate, α-KG: α-ketoglutarate, Suc-CoA: succinyl-CoA, Suc: succinate.