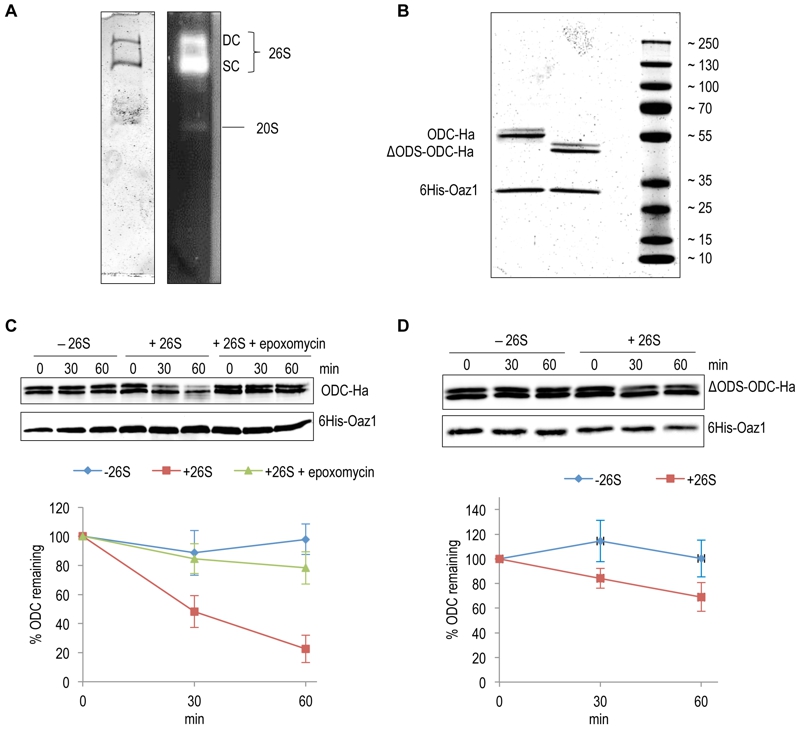
FIGURE 2: In vitro characterization of antizyme-mediated and ODS-dependent degradation of ODC.
(A) Flag-tagged proteasome affinity-purified from yeast cells was analyzed by native-PAGE and Coomassie staining (left) or activity staining by overlay with the fluorogenic peptide Suc-LLVY-AMC (right). Proteasomes in this preparation were either doubly-capped (DC) with RPs on both sides of the core particle (CP), or singly-capped (SC) with only one RP attached to the CP. 20S CPs without any RPs attached to them were also present in the preparation.
(B) SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining of 6His-Oaz1 co-purified from E. coli cells as heterodimer either with full length ODC (ODC-2xHa) or with N-terminally truncated ODC lacking the first 47 residues (ΔODS-ODC-2xHa).
(C) In vitro degradation assays with purified 26S proteasomes and purified ODC-Oaz1 heterodimer as a substrate showing the degradation of ODC over time. 50 ng of ODC-Oaz1 heterodimer and 3 µg of 26S were mixed in 15 µL resulting in starting concentrations, respectively, of 40 nM and 80 nM. As controls, otherwise identical samples were assayed without 26S proteasome (-26S), or with the proteasome inhibitor epoxomycin. Two bands (full-length ODC-2xHa and a truncated derivative) were detected with the anti-Ha antibody, and both forms showed similar turnover rates. Therefore both bands were quantified together. In the resulting graph, values for the 0 time points were set to 100%. Error bars, s.d.; n = 3.
(D) Experiments were performed as described for Fig. 2B, except that ΔODS-ODC-2xHa was used instead of full length ODC.