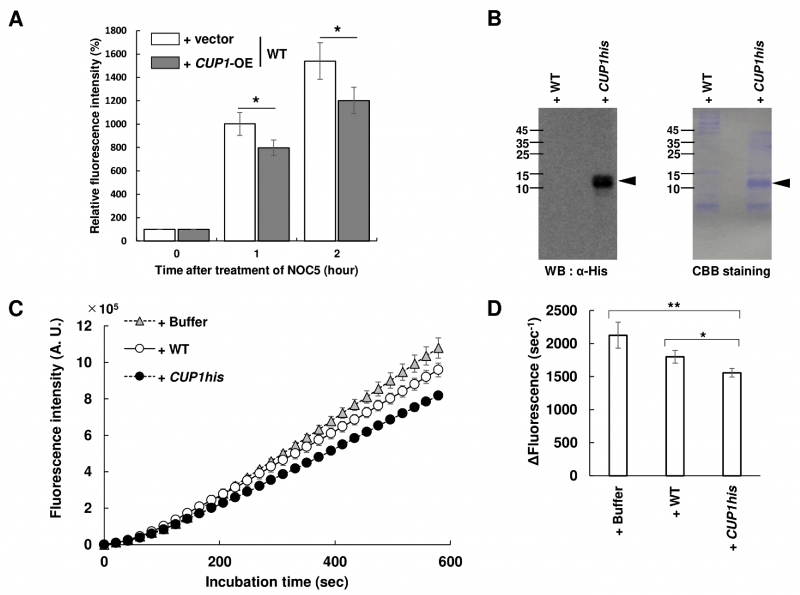
FIGURE 2: NO degradation by Cup1 in S. cerevisiae cells. (A) The intracellular NO level in S. cerevisiae cells was quantified. The WT strain harboring empty vector or overexpressing CUP1 was cultured to the early exponential phase in SD medium (pH 6.0) at 25°C and then treated with DAF-FM DA. Subsequently, cells were exposed to NOC-5, followed by FCM. The relative fluorescence intensity was calculated with the fluorescence at 0 hour after the beginning of incubation as 100%. The means and standard deviations from at least three independent experiments were shown. Statistical significance of differences was analyzed by Student's t test (*p < 0.05, WT vs. CUP1-OE). (B, C, D) The yeast WT strain harboring a empty vector or the cup1Δ strain overexpressing CUP1his was shown as WT or CUP1his, respectively. (B) Detection and quantification of Cup1-His in the CUP1his strain. WT and CUP1his strain were cultured to the exponential phase in SD medium at 25°C, and the cell-free lysate was analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-His antibody or CBB staining. An arrowhead in each picture indicates Cup1-His. (C) The inhibition of the time-dependent fluorescence increase mediated by Cup1-His. Each NOC-5 was reacted with DAF-FM in the absence or presence of the cell-free lysate from WT or CUP1his strain, and then the fluorescence intensity was monitored over time. The means and standard deviations from three independent experiments were shown. (D) The rate of fluorescence increases from 100 sec to 600 sec after reaction started were calculated. The means and standard deviations from three independent experiments were shown. Statistical significance in differences was analyzed by Student's t test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.