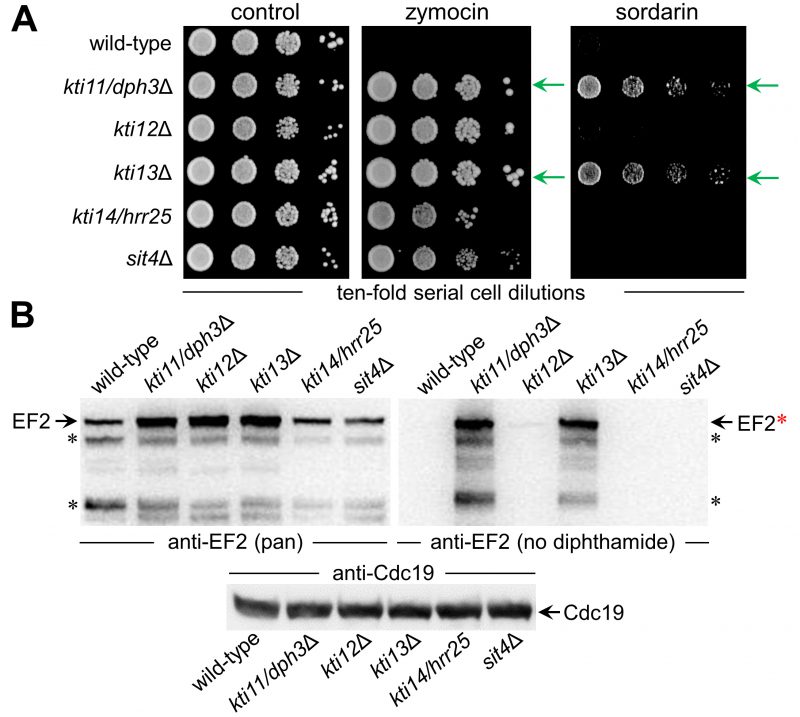
FIGURE 2: Among genes involved in Elongator regulation and tRNA modification, KTI11 and KTI13 also function in EF2 modification. (A) Growth assays in response to zymocin (0.02% [v/v]) or sordarin (9 µg/mL) and diagnostic for tRNA or diphthamide modifciation defects, respectively. Dilutions of cells with indicated genotypes were incubated at 30°C for 3 days. Note, that while all ktiΔ and sit4Δ mutants resist growth inhibition by Elongator-dependent tRNase zymocin, only kti11/dph3Δ and kti13Δ cells are protected (green arrows) against diphthamide-dependent EF inhibitor sordarin. (B) Western blot analysis of total cell extracts from strains with genotypes as in A in order to profile their amounts of total EF2 and unmodified EF2 using anti-EF2(pan) (left panel) and anti-EF2(no diphthamide) antibodies (right panel), respectively. Black asterisks (left & right panels) denote EF2 degradation products, the red asterisk indicates full-length unmodified EF2 (right panel). The anti-Cdc19 antibody (bottom panel) was used as loading control. Note the anti-EF2(no diphthamide) Western blot (right panel) detects unmodified EF2 pools for kti11/dph3Δ and kti13Δ cells indicative for diphthamide defects.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.