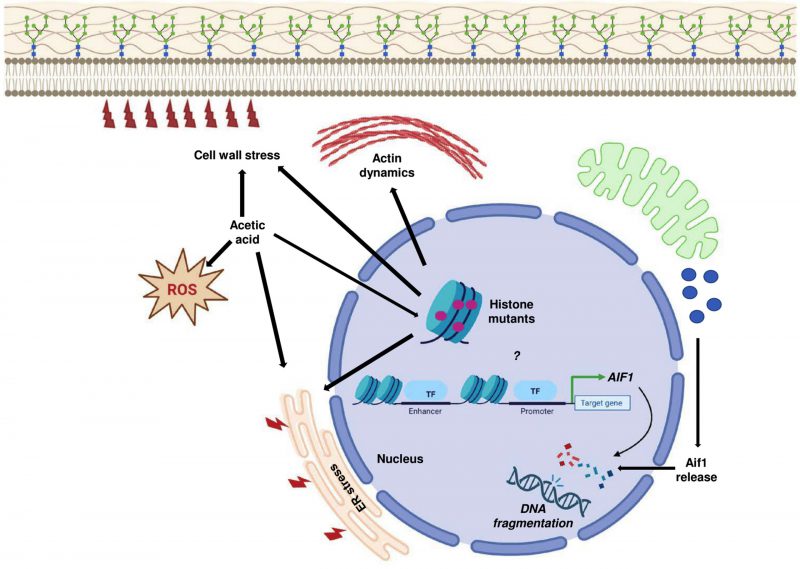
FIGURE 10: Acetic acid response in histone mutants. The sensitive histone mutants exhibit induced expression levels of AIF1, which probably reflects the increased apoptotic stress in the mutants after acetic acid treatment. Thus, the increased gene expression may be an indirect consequence of increased stress in the mutant cells or maybe because of the importance of the mutated histone residue in regulating the gene. Acetic acid-mediated ER and cell wall stress may exacerbate the effect on histone mutants with pre-existing sensitivity towards ER stress or cell wall stress. Pronounced stress by acetic acid in the mutants increases the ROS and pre-existing defective actin dynamics together with all the factors that cause sensitivity of the histone mutants in acetic acid.
By continuing to use the site, you agree to the use of cookies. more information
The cookie settings on this website are set to "allow cookies" to give you the best browsing experience possible. If you continue to use this website without changing your cookie settings or you click "Accept" below then you are consenting to this. Please refer to our "privacy statement" and our "terms of use" for further information.