Back to article: Chlamydia pneumoniae is present in the dental plaque of periodontitis patients and stimulates an inflammatory response in gingival epithelial cells
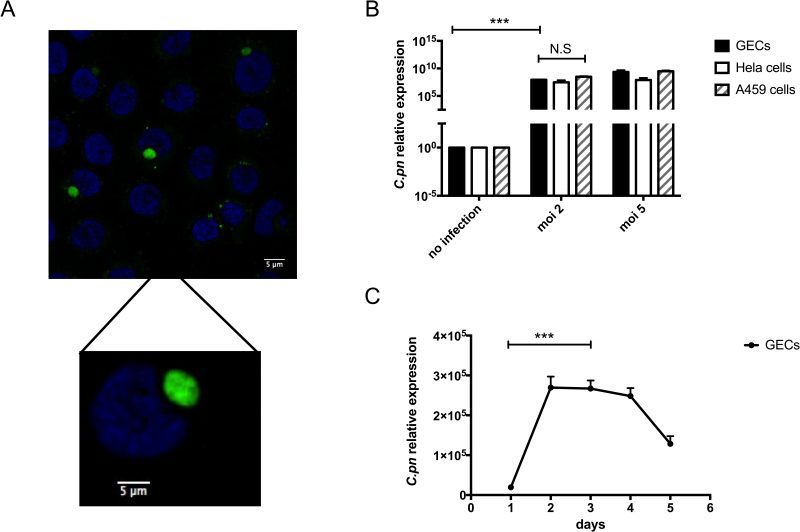
FIGURE 2: C. pneumoniae infects human gingival epithelial cells. (A). Gingival epithelial cells (GECs), infected four days with C. pneumoniae at MOI of 5, were incubated with a FITC-conjugated mAb against Chlamydia (green) for 15 minutes, and the nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (blue). (B) qPCR of hGECs, HeLa cells, and A549 cells infected with C. pneumoniae for two days at MOI of 0, 2 and 5. qPCR assays were performed in triplicate, n = 4 independent experiments. Error bars represent ± SD; 2-sided, paired Student's t test, ***P < 0.001. (C) GECs were infected with C. pneumoniae at MOI of 5 and infected samples were collected 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days post-infection for qPCR analysis. Assays were performed in triplicates, n = 5 independent experiments. Error bars represent ± SD; 2-sided, paired Student's t test, ***P < 0.001.