Back to article: Gut microbial metabolites in depression: understanding the biochemical mechanisms
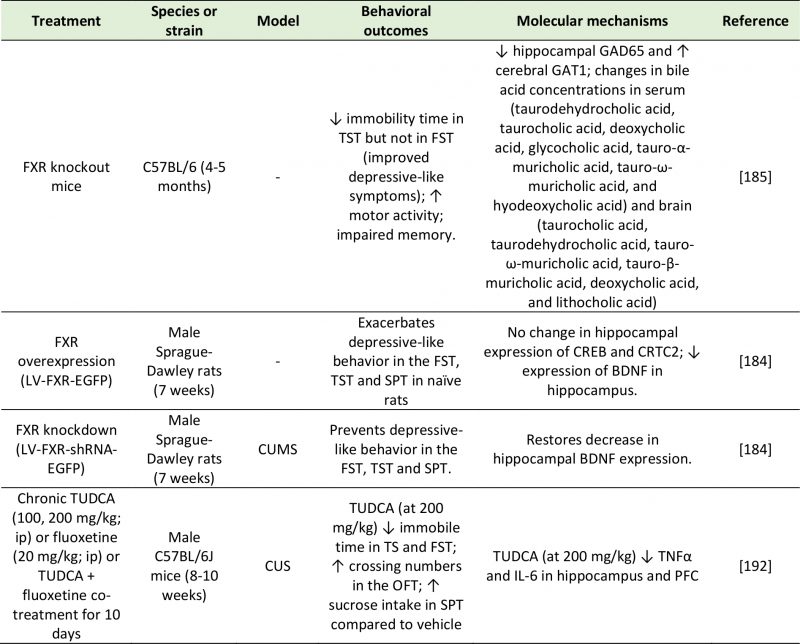
TABLE 6. Studies investigating the effects of bile acids on depressive-like behavior.
BDNF: Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor; CREB: Camp Response Element-Binding Protein; CRTC2: CREB-Regulated Transcription Coacti-vator 2; CUMS: Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress; CUS: Chronic Unpredictable Stress; FST: Forced-Swim Test; FXR: Farnesoid X Receptor; GAD65: Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 65; GAT1: GABA Transporter 1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; OFT: Open Field Test; SPT: Sucrose Preference Test; Tnfα: Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha; TST: Tail Suspension Test; TUDCA: Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid.
184. Chen WG, Zheng JX, Xu X, Hu YM, and Ma YM (2018). Hippocampal FXR plays a role in the pathogenesis of depression: A preliminary study based on lentiviral gene modulation. Psychiatry Res 264: 374–379. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.04.025
185. Huang F, Wang T, Lan Y, Yang L, Pan W, Zhu Y, Lv B, Wei Y, Shi H, Wu H, Zhang B, Wang J, Duan X, Hu Z, and Wu X (2015). Deletion of mouse FXR gene disturbs multiple neurotransmitter systems and alters neurobehavior. Front Behav Neurosci 9: 70. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00070
192. Lu X, Yang RR, Zhang JL, Wang P, Gong Y, Hu W feng, Wu Y, Gao M hui, and Huang C (2018). Tauroursodeoxycholic acid produces antidepressant-like effects in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression via attenuation of neuroinflammation, oxido-nitrosative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 32(4): 363–377. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12367