Back to article: Diverse conditions support near-zero growth in yeast: Implications for the study of cell lifespan
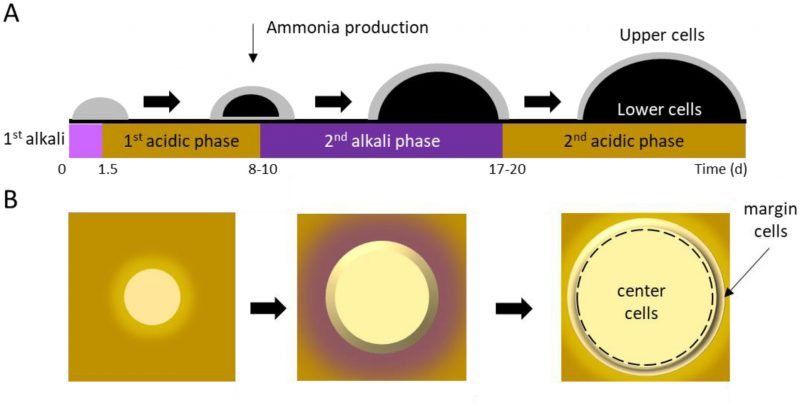
FIGURE 2: Yeast colonies transition through alkali (pH ∼6.8) and acidic (pH ∼5.2) phases, causing the area around a colony to change in color from yellow to purple and back again on agar containing Bromocresol purple. The pH changes contribute to cellular differentiation in both the vertical (A) and horizontal (B) dimensions. Gray indicates healthy, dividing cells and black indicates non-dividing cells.