Back to article: Guidelines for DNA recombination and repair studies: Cellular assays of DNA repair pathways
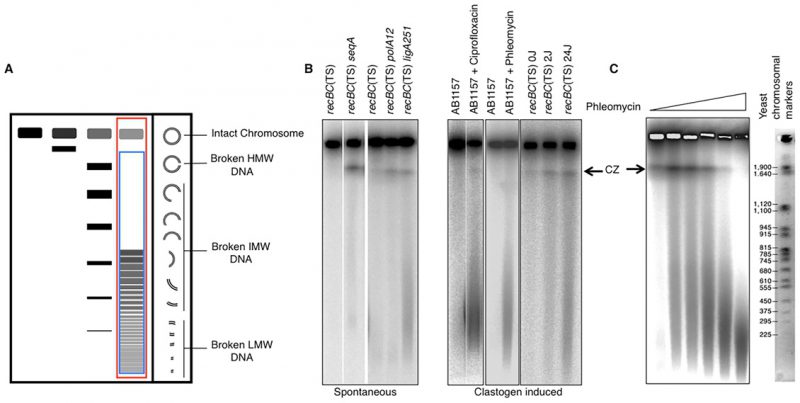
FIGURE 8: Fragmentation of bacterial chromosomes under various conditions. (A) Schematic representation of size-dependent migration of linear DNA through PFGs. Note that the intact circular chromosome stays in the wells. Chromosomal fragmentation is quantified as the percentage of the total signal (well+lane, red rectangle) that enters the lane (blue rectangle), that is: [Signal in lanes x 100 / total signal (well+lane)]. HMW, high molecular weight (≥2 mbp); IMW, Intermediate molecular weight (0.2 – 2.0 mbp); LMW, low molecular weight (≤0.2 mbp). (B) Spontaneous and clastogen-induced chromosomal fragmentation in E. coli. Typically, chromosomal fragmentation is detected in the recBC mutant, deficient both in repair of DSBs and in degradation of linear DNA. However, when fragmentation is massive, it can be detected in wild type cells (such as ciprofloxacin- or phleomycin-induced fragmentation in AB1157 in these examples). Spontaneous fragmentation is measured under conditions when the recBC(Ts) mutants carry additional defects in SeqA, DNA polymerase I or DNA ligase [165, 167]. Clastogen-induced fragmentation is observed upon exposure to phleomycin and ciprofloxacin. Ultraviolet light, which affects only one strand of DNA, still causes significant fragmentation in recBC(Ts) background [166]. CZ, compression zone. (C) Pulsed field gel electrophoresis can be used to calculate the density of breaks in the chromosomal DNA if the average size of the resulting chromosomal fragments is measured.
165. Rotman E, Khan SR, Kouzminova E, Kuzminov A (2014). Replication fork inhibition in seqA mutants of Escherichia coli triggers replication fork breakage. Mol Microbiol 13(4): 367–374. 93(1): 50-64. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12638
166. Khan SR, Kuzminov A (2012). Replication forks stalled at ultraviolet lesions are rescued via RecA and RuvABC protein-catalyzed disintegration in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 287(9): 6250-6265. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322990
167. Khan SR, Kuzminov A (2013). Trapping and breaking of in vivo nicked DNA during pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 443(2): 269-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2013.06.001