Back to article: Guidelines for DNA recombination and repair studies: Cellular assays of DNA repair pathways
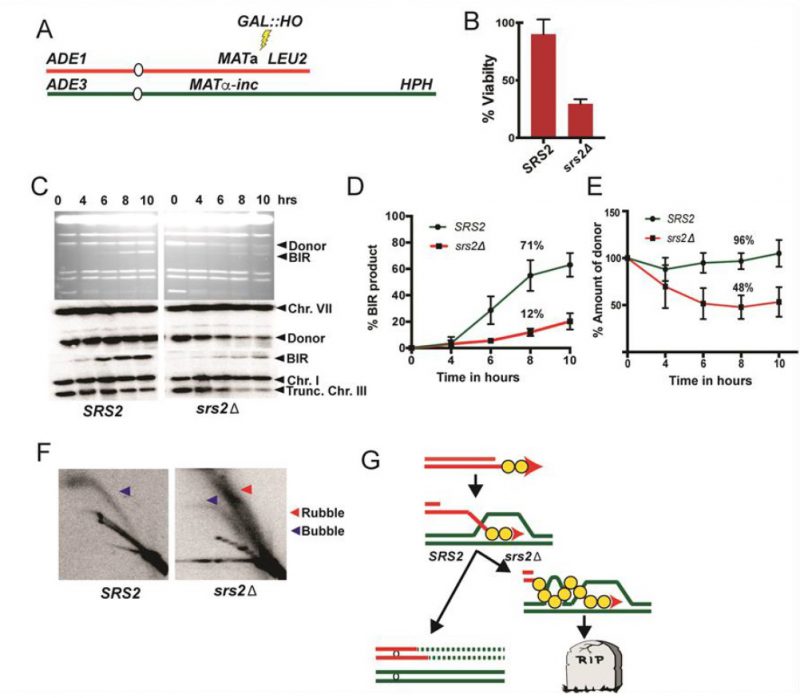
FIGURE 12: Detection of toxic recombination intermediates during BIR in yeast. (from data in Elango et al [214] published under open access under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License) (A) Experimental system to study BIR. BIR is initiated by DSB introduced by galactose-induced HO endonuclease at MATa locus in yeast disomic for Chr. III (B) Cell viability following DSB induction (%). (C) BIR kinetics analyzed by CHEF gel using cells taken at indicated time points following DSB induction. Upper panel: CHEF gels stained with Ethidium Bromide. Subsequent panels below show Southern blot analysis using ADE1-specific, and ADE3-specific probes, hybridizing to the recipient and the donor chromosomes, respectively. (D) Quantification of BIR product. (E) Quantification of donor chromosome entering the gel. (F) 2D gel analysis of BIR intermediates in SRS2 and srs2Δ at 7h following DSB induction. Genomic DNA was digested with BglII to detect intermediates at 24 kb position. Intermediates were detected using a probe specific to the 24 kb position of Chr III. Blue arrowheads denote bubble arc intermediates and red arrowhead denotes ‘rubble' structure. (G) The schematics shows broken recipient chromosome (red) invading unbroken homologous donor (green). Repair DNA synthesis is initiated and progresses by a migrating bubble. In SRS2: successful completion of BIR with conservative inheritance of newly synthesized DNA. In srs2Δ : formation of toxic joint molecules via unscheduled invasion of ssDNA located behind the BIR bubble into homologous chromosome leading to cell death.
214. Elango R, Sheng Z, Jackson J, DeCata J, Ibrahim Y, Pham NT, Liang DH, Sakofsky CJ, Vindigni A, Lobachev KS, Ira G, Malkova A (2017). Break-induced replication promotes formation of lethal joint molecules dissolved by Srs2. Nat Commun > 8(1): 1790. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01987-2