Back to article: Depletion of SNAP-23 and Syntaxin 4 alters lipid droplet homeostasis during Chlamydia infection
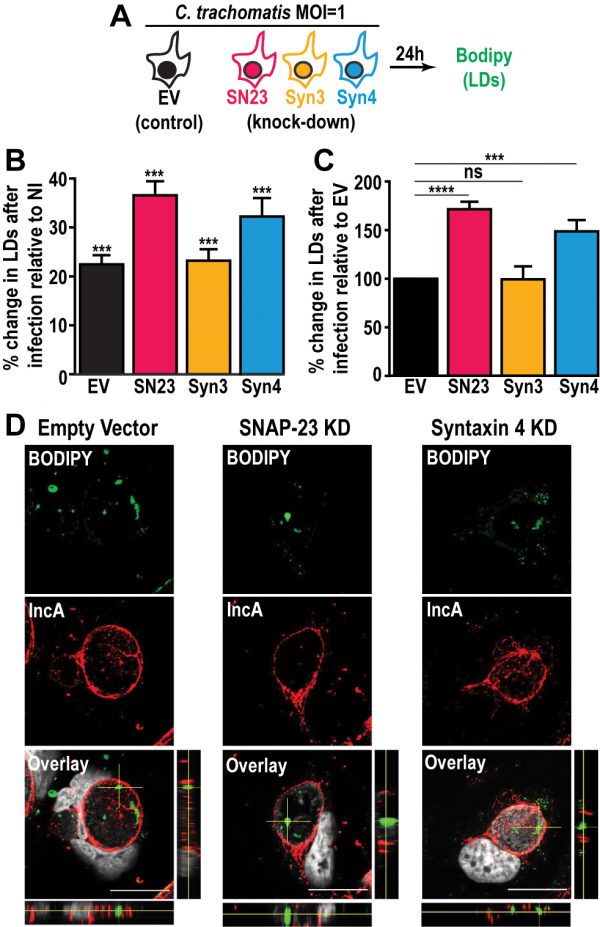
FIGURE 3: Depletion of SNAP-23 and Syntaxin 4 increases LD content during Chlamydia infection without affecting LD internalization into the inclusion lumen. (A) Experimental design. SN23 = SNAP-23, Syn3 = Syntaxin 3, Syn4 = Syntaxin 4, LDs = lipid droplets, MOI = multiplicity of infection. (B and C) Cells were either infected with mCherry-expressing C. trachomatis L2 at a MOI of 1 or mock-infected with DMEM for 24 h. The cells were then stained with BODIPY and fixed. BODIPY intensity was measured by flow cytometry. For the infected samples only the mCherry-positive population (infected cells) was measured. (B) Graph represents the average percent increase in BODIPY staining relative to non-infected cells from at least three independent experiments ± the standard deviation. Asterisk (***) denotes a p value < 0.001. (C) Graph represents the average increase in BODIPY staining relative to infected empty vector control cells from at least three independent experiments ± the standard deviation. The percent increase in BODIPY staining following infection for the empty vector control cell line was arbitrarily set at 100% and represents 121.41% ± 4.92. Values for the KD cells were then normalized to the EV control. Asterisk (***) denotes a p value < 0.001 and (****) denotes a p value <0.0001. ns = not significant. (D) The indicated cell lines were infected with C. trachomatis L2 at a MOI of 0.5 for 30 h. The cells were then fixed and stained with anti-IncA antibody (red) and BODIPY 493/503 (green). Hoechst was used to label DNA (gray). Images are taken from a single plane of confocal z-stacks. Orthogonal XZ and YZ views are shown next to and below the overlay image, respectively. Scale bar = 20 μm. KD = knock down.