Back to article:
Guidelines for DNA recombination and repair studies: Mechanistic assays of DNA repair processes
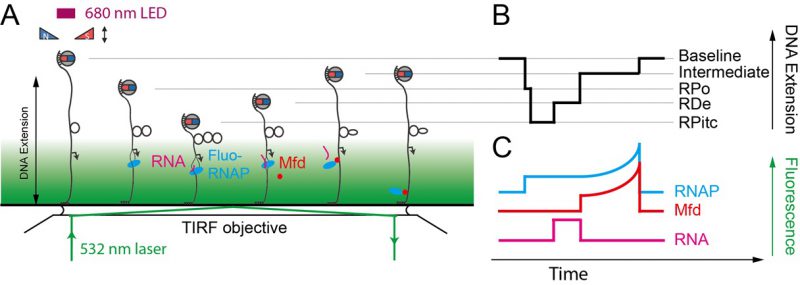
FIGURE 6: Sketch of the NanoCOSM assay (for nanomanipulation and colocalization of single-molecules) as applied to TCR. (A) An exponentially-decaying total-internal reflection field is added to the magnetic trap by introducing a laser line into the system (green line) such that it impinges, collimated, upon the glass-water interface of the sample at or above the critical angle σc=sin−1(nwater/nglass) − here σc is the beam angle relative to axis normal to the interface, and nwater and nglass are the indices of refraction of water and glass, respectively. (B) Magnetic trapping of the DNA allows one to monitor transcription-coupled repair as remodeling by Mfd of RNAP stalled on a DNA lesion and the concomitant formation of an intermediate extension state (labeled ‘intermediate'). The molecular composition of the mechanically-defined intermediate state naturally remains ambiguous based on the magnetic trapping data; it could include Mfd, or RNAP, or both. (C) Simultaneous single-molecule fluorescence detection of fluorescently labeled components of the reaction lifts the ambiguity and allows one to enumerate the components present on the DNA at each stage of the repair reaction. These experiments show that Mfd remodels RNAP, causing it to lose hold of the nascent RNA, but that thereafter the RNAP stays associated with Mfd. Fluorescence signatures of RNAP and Mfd increase after remodeling because Mfd remains on the DNA and translocates in the same direction as initial transcription, i.e. towards the surface, transporting its associated RNAP along as this permits the translocase to remain tightly bound to the DNA and highly processive.